Krane is a simple Kubernetes RBAC static analysis tool. It identifies potential security risks in K8s RBAC design and makes suggestions on how to mitigate them. Krane dashboard presents current RBAC security posture and lets you navigate through its definition.
Features
- RBAC Risk rules – Krane evaluates a set of built-in RBAC risk rules. These can be modified or extended with a set of custom rules.
- Portability – Krane can run in one of the following modes:
- Locally as a CLI or docker container.
- In CI/CD pipelines as a step action detecting potential RBAC flaws before it gets applied to the cluster.
- As a standalone service continuously analysing state of RBAC within a Kubernetes cluster.
- Reporting – Krane produces an easy to understand RBAC risk report in machine-readable format.
- Dashboard – Krane comes with a simple Dashboard UI helping you understand in-cluster RBAC design. Dashboard presents high-level overview of RBAC security posture and highlights detected risks. It also allows for further RBAC controls inspection via faceted tree and graph network views.
- Alerting – It will alert on detected medium and high severity risks via its Slack integration.
- RBAC in the Graph – Krane indexes entirety of Kubernetes RBAC in a local Graph database which makes any further ad-hoc interrogating of RBAC data easy, with arbitrary CypherQL queries.
Local Quick Start
Get started locally with Docker Compose.
Prerequisites
It is assumed that you have docker running on your local machine. Install docker-compose if you haven’t already.
Run Krane Locally
Krane depends on RedisGraph. docker-compose stack defines all what’s required to build and run Krane service locally. It’ll also take care of its RedisGraph dependency.
docker-compose up -d
Krane docker image will be pre-built automatically if not already present on local machine.
Note that when running docker-compose locally, Krane won’t start RBAC report and dashboard automatically. Instead, the container will sleep for 24h by default – this value can be adjusted in docker-compose.override.yml. Exec into a running Krane container to run commands. Local docker-compose will also mount kube config (~/.kube/config) inside the container enabling you to run reports against any Kubernetes clusters to which you already have access to.
#Exec into a running Krane container
docker-compose exec krane bash
#Once in the container you can start using krane commands. Try krane -help.
$ krane -h
To inspect what services are running and the associated ports:
docker-compose ps
To stop Krane and its dependency services:
docker-compose down
Usage Guide
Commands
$ krane –help
NAME:
krane
DESCRIPTION:
Kubernetes RBAC static analysis & visualisation tool
COMMANDS:
dashboard Start K8s RBAC dashboard server
help Display global or [command] help documentation
report Run K8s RBAC report
GLOBAL OPTIONS:
-h, –help
Display help documentation
-v, –version
Display version information
-t, –trace
Display backtrace when an error occurs
AUTHOR:
Marcin Ciszak marcin.ciszak@appvia.io – Appvia Ltd
Generate RBAC report
With local kubectl context
To run a report against a running cluster you must provide a kubectl context
krane report -k <context>
You may also pass -c <cluster-name> flag if you plan to run the tool against multiple clusters and index RBAC graph separately for each cluster name.
From RBAC files stored in directory
To run a report against local RBAC yaml/json files, provide a directory path
krane report -d </path/to/rbac-directory>
NOTE: Krane expects the following files (in either YAML or JSON format) to be present in specified directory path:
- psp
- roles
- clusterroles
- rolebindings
- clusterrolebindings
Inside a Kubernetes cluster
To run a report from a container running in Kubernetes cluster
krane report –incluster
NOTE: Service account used by Krane will require access to RBAC resources. See Prerequisites for details.
In CI/CD pipeline
To validate RBAC definition as a step in CI/CD pipeline
krane report –ci -d </path/to/rbac-directory>
NOTE: Krane expects certain naming convention to be followed for locally stored RBAC resource files. See section above. In order to run krane commands it’s recommended that CI executor references quay.io/appvia/krane:latest docker image.
CI mode is enabled by --ci flag. Krane will return non zero status code along with details of breaking risk rules when one or more dangers have been detected.
Visualisation Dashboard
To view RBAC facets tree, network graph and latest report findings you need to start dashboard server first.
krane dashboard
Cluster flag -c <cluster-name> may be passed if you want to run the dashboard against specific cluster name. Dashboard will look for data related to specified cluster name which is cached on the file system.
Command above will start local web server on default port 8000, and display the dashboard link.
Architecture
RBAC Data indexed in a local Graph database
Krane indexes RBAC entites in RedisGraph. This allows us to query network of dependencies efficiently and simply using subset of CypherQL supported by RedisGraph.
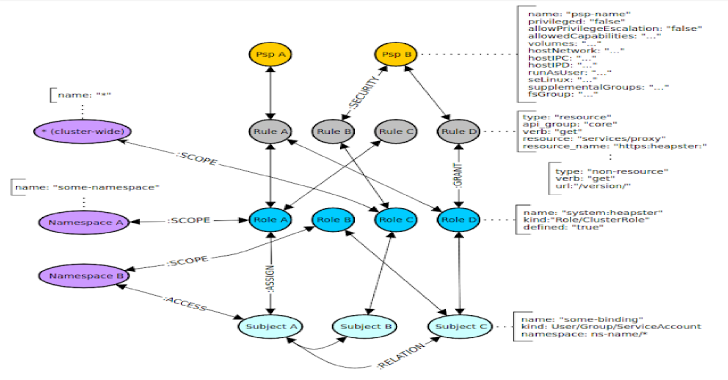
Nodes
The following nodes are created in the Graph for the relevant RBAC objects:
Psp– A PSP node containing attributes around the pod security policy.Rule– Rule node represents access control rule around Kubernetes resources.Role– Role node represents a given Role or ClusterRole.kindattribute defines type of role.Subject– Subject represents all possible actors in the cluster (kind: User, Group and ServiceAccount)Namespace– Kubernetes Namespace node.
Edges
:SECURITY– Defines a link between Rule and Psp nodes.:GRANT– Defines a link between Role and Rule associated with that role.:ASSIGN– Defines a link between an Actor (Subject) and given Role/ClusterRole (Role node).:RELATION– Defines a link between two different Actor (Subject) nodes.:SCOPE– Defines a link between Role and Namespace nodes.:ACCESS– Defines a link between Subject and Namespace nodes.:AGGREGATE– Defines a link between ClusterRoles (one ClusterRole aggregates another)A-(aggregates)->B:COMPOSITE– Defines a link between ClusterRoles (one ClusterRole can be aggregated in another)A<-(is a composite of)-B
All edges are bidirectional, which means graph can be queried in either direction. Only exceptions are :AGGREGATE and :COMPOSITE relations which are uni-directional, though concerned with the same edge nodes.
Querying the Graph
In order to query the graph directly you can exec into a running redisgraph container, start redis-cli and run your arbitrary queries. Follow official instructions for examples of commands.
You can also query the Graph from Krane console. First exec into running Krane container, then
#Start Krane console – this will open interactive ruby shell with Krane code preloaded
console
#Instantiate Graph client
graph = Krane::Clients::RedisGraph.client cluster: ‘default’
#Run arbitrary CypherQL query against indexed RBAC Graph
res = graph.query(%Q(
MATCH (r:Rule {resource: “configmaps”, verb: “update”})<-[:GRANT]-(ro:Role)<-[:ASSIGN]-(s:Subject)
RETURN s.kind as subject_kind, s.name as subject_name, ro.kind as role_kind, ro.name as role_name))
#Print the results
res.print_resultset
Results…
+—————-+——————————–+———–+————————————————+
| subject_kind | subject_name | role_kind | role_name |
+—————-+——————————–+———–+————————————————+
| ServiceAccount | bootstrap-signer | Role | system:controller:bootstrap-signer |
| User | system:kube-controller-manager | Role | system::leader-locking-kube-controller-manager |
| ServiceAccount | kube-controller-manager | Role | system::leader-locking-kube-controller-manager |
| User | system:kube-scheduler | Role | system::leader-locking-kube-scheduler |
| ServiceAccount | kube-scheduler | Role | system::leader-locking-kube-scheduler |
+—————-+——————————–+———–+————————————————+
Note: Example query above will select all Subjects with assigned Roles/ClusterRoles granting access to update configmaps.
Configuration
RBAC Risk Rules
RBAC risk rules are defined in the Rules file. The structure of each rule is largely self-explanatory. Built-in set can be expanded / overridden by adding extra custom rules to the Cutom Rules file.
Risk Rule Macros
Macros are “containers” for a set of common/shared attributes, and referenced by one or more risk rules. If you choose to use macro in a given risk rule you would need to reference it by name, e.g. macro: <macro-name>. Note that attributes defined in referenced macro will take precedence over the same attributes defined on the rule level.
Macro can contain any of the following attributes:
query– RedisGraph query. Has precedence overtemplate. Requireswriterto be defined.writer– Writer is a Ruby expression used to formatqueryresult set. Writer has precedence overtemplate.template– Built-in query/writer template name. Ifquery&writerare not specified then chosen query generator will be used along with matching writer.
Risk Rule attributes
Rule can contain any of the following attributes:
id[Required] Rule id is a unique rule identifier.group_title[Required] Title applying to all items falling under this risk check.severity[Required] Severity, as one of :danger, :warning, :info.info[Required] Textual information about the check and suggestions on how to mitigate the risk.query[Conditonal] RedisGraph query.- Has precedence over
template. Requireswriterto be defined.
- Has precedence over
writer[Conditonal] Writer is a Ruby expression used to format query result set.- Writer has precedence over
template. Requiresqueryto be defined.
- Writer has precedence over
template[Conditonal] Built-in query/writer template name. Ifquery&writerare not specified then chosen query generator will be used along with matching writer.- Some built-in templates require
match_rulesattribute to be specified on individual rule level in order to build correct query. Templates currently requiring it:- risky-role – Builds multi-match graph query based on the access rules specified by
match_rules. Generated graph query returns the following columns:- role_name
- role_kind
- namespace_name (an array is returned if multiple items returned)
- risky-role – Builds multi-match graph query based on the access rules specified by
- Some built-in templates require
match_rules[Conditonal] Required whentemplaterelies on match rules in order to build a query.
Example:
match_rules:
– resources: [‘cronjobs’]
verbs: [‘update’]
Attributes and values follow Kubernetes RBAC role specification.
custom_params [Optional] List of custom key-value pairs to be evaluated and replaced in a rule query and writer representation.
Example:
custom_params:
– attrA: valueA
– attrB: valueB
- Template placeholders for the keys above
{{attrA}}and{{attrB}}will be replaced withvalueAandvalueBrespectively.
threshold[Optional] Numeric value. When definied this will become available as template placeholder{{threshold}}in thewriterexpression.macro[Optional] Reference to common parameters defined in a named macro.disabled[Optional] When set totrueit’ll disable given rule and exclude it from evaluation. By default all rules are enabled.
Risk Rule examples
Explicit query & writer expression
– id: verbose-rule-example
group_title: Example rule
severity: :danger
info: Risk description and instructions on how to mitigate it goes here
query: |
MATCH
(s:Subject)-[:ACCESS]->(ns:Namespace)
WHERE
NOT s.name IN {{whitelist_subject_names}}
RETURN
s.kind as subject_kind,
s.name as subject_name,
COLLECT(ns.name) as namespace_names
ORDER BY
subject_kind,
subject_name,
namespace_names DESC
threshold: 2
writer: |
if result.namespace_names.count > {{threshold}}
“#{result.subject_kind} #{result.subject_name} can access namespaces: #{result.namespace_names.join(‘, ‘)}”
end
disabled: true
The example above explicitly defines a graph query which is used to evaluate RBAC risk, and a writer expression used to format query result set. The query simply selects all Subjects (excluding whitelisted) and Namespaces to which they have access to. Note that the result set will only include Subjects having access to more than 2 Namespaces (Noticed threshold value there?). Last writer‘s expression will be captured as formatted result item output.
writer can access the result set item via result object with methods matching elements returned by the query, e.g. result.subject_kind, result.subject_name etc.
Note:
{{threshold}}placeholder in thewriterexpression will be replaced by the rule’sthresholdkeyword value.{{whitelist_subject_names}}represents a custom field which will be interpolated with Whitelist values defined for a given ruleid. If a placeholder field name is not defined in the whitelist it’ll be substituted with an empty array['']by default. Read more on whitelisting below.
Templated Risk Rule
Built-in templates simplify risk rule definition significantly, however, they are designed to extract specific kind of information and may not be a good fit for your custom rules. If you find yourself reusing the same query or writer expressions across multiple rules, you should consider extracting those to a macro and reference it in your custom rules to DRY them up.
– id: risky-any-verb-secrets
group_title: Risky Roles/ClustersRoles allowing all actions on secrets
severity: :danger
info: Roles/ClusterRoles allowing all actions on secrets. This might be dangerous. Review listed Roles!
template: risky-role
match_rules:
– resources: [‘secrets’]
verbs: [‘*’]
Example above shows one of the built-in rules. It references risky-role template which upon processing will expand the rule by injecting query and writer expressions before rule evalutation triggers. match_rules will be used to build appropriate match query.
RBAC Risk Whitelist
Optional whitelist contains a set of custom defined attribute names and respective (whitelisted) values.
Whitelist attributes
Attribute names and their values are arbitrary. They are defined in the Whitelist file and divided into three separate sections:
global– Top level scope. Custom attributes defined here will apply to all Risk Rules regardless of the cluster name.common– Custom attributes will be scoped to specific Risk Ruleidregardless of the cluster name.cluster(with nested list of cluster names) – Custom attributes will apply to specific Risk Ruleidfor a given cluster name.
Each Risk Rule, upon evaluation, will attempt to interpolate all parameter placeholders used in the query, e.g. {{your_whitelist_attribute_name}}. If a placeholder parameter name (i.e. a name between the double curly brackets) matches any of the whitelisted attribute names for that Risk Rule id, it will be replaced with its calculated value. If no values are found for a given placeholder, it’ll be substituted with [''].
Whitelist examples
Example whitelist below produces the following placeholder-key => value mapping for a Risk Rule with id attribute value matching “some-risk-rule-id”
{{whitelist_role_names}} => [‘acp:prometheus:operator’]
{{whitelist_subject_names}} => [‘privileged-psp-user’, ‘another-user’]
The placeholder keys above, when used in the custom graph queries, will be replaced by their respective values upon Risk Rule evaluation.
Example:
rules:
global: # global scope – applies to all risk rule and cluster names
whitelist_role_names: # custom attribute name
– acp:prometheus:operator # custom attribute values
common: # common scope – applies to specific risk rule id regardless of cluster name
some-risk-rule-id: # this corresponds to risk rule id defined in config/rules.yaml
whitelist_subject_names: # custom attribute name
– privileged-psp-user # custom attribute values
cluster: # cluster scope – applies to speciifc risk rule id and cluster name
default: # example cluster name
some-risk-rule-id: # risk rule id
whitelist_subject_names: # custom attribute nane
– another-user # custom attribute values
Kubernetes Deployment
Krane can be deployed to a local or remote Kubernetes clusters easily.
K8s Prerequisites
Kubernetes namespace, service account along with appropriate RBAC must be present in the cluster. See the Prerequisites for reference.
Default Krane entrypoint executes bin/in-cluster-run which waits for RedisGraph instance to become available before starting RBAC report loop and dashboard web server.
You may control certain aspects of in-cluster execution with the following environment variables:
KRANE_REPORT_INTERVAL– Defines interval in seconds for RBAC static analysis report run. Default:300(in seconds, i.e. 5 minutes).KRANE_REPORT_OUTPUT– Defines RBAC risk report output format. Possible values:json,:yaml,:none. Default::json.
Local or Remote K8s Cluster
If your K8s cluster comes with built-in Compose-on-Kubernetes controller support (docker-desktop supports it by default), then you can deploy Krane and its dependencies with a single docker stack command:
docker stack deploy \
–orchestrator kubernetes \
–namespace krane \
–compose-file docker-compose.yml \
–compose-file docker-compose.k8s.yml krane
Note: Make sure your current kube context is set correctly prior to running the command above!
The application Stack should be now deployed to a Kubernetes cluster and all services ready and exposed. Note that Krane will automatically start its report loop and dashboard server.
$ docker stack services –orchestrator kubernetes –namespace krane krane
ID NAME MODE REPLICAS IMAGE PORTS
0de30651-dd5 krane_redisgraph replicated 1/1 redislabs/redisgraph:1.99.7 *:6379->6379/tcp
aa377a5f-62b krane_krane replicated 1/1 quay.io/appvia/krane:latest *:8000->8000/tcp
Check your Kubernetes cluster RBAC security posture by visiting
http://localhost:8000
Note that for remote cluster deployments you’ll likely need to port-forward Krane service first
kubectl –context=my-remote-cluster –namespace=krane port-forward svc/krane 8000
To delete the Stack
docker stack rm krane \
–orchestrator kubernetes \
–namespace krane
Alternatively, deploy with kubectl:
kubectl create \
–context docker-desktop \
–namespace krane \
-f k8s/redisgraph-service.yaml \
-f k8s/redisgraph-deployment.yaml \
-f k8s/krane-service.yaml \
-f k8s/krane-deployment.yaml
Note that Krane dashboard services are not exposed by default!
kubectl port-forward svc/krane 8000 \
–context=docker-desktop \
–namespace=krane
#Open Krane dashboard
http://localhost:8000
You can find the example deployment manifests in k8s directory.
Modify manifests as required for your deployments making sure you reference the correct version of Krane docker image in its deployment file. See Krane Docker Registry for available tags, or just use latest.
Notifications
Krane will notify you about detected anomalies of medium and high severity via its Slack integration.
To enable notifications specify Slack webhook_url & channel in the config/config.yaml file, or alternatively set both SLACK_WEBHOOK_URL and SLACK_CHANNEL environment variables. Environment variables will take precedence over config file values.
Local Development
This section describes steps to enable local development.
Setup
Install Krane code dependencies with
./bin/setup
Dependencies
Krane depends on RedisGraph. docker-compose is the quickest way to get Krane‘s dependencies running locally.
docker-compose up -d redisgraph
To inspect RedisGraph service is up:
docker-compose ps
To stop services
docker-compose down
Development
At this point you should be able to modify Krane codebase and test results by invoking commands in local shell.
./bin/krane –help # to get help
./bin/krane report -k docker-desktop # to generate your first report for
# local docker-desktop k8s cluster
To enable Dashboard UI local development mode
cd dashboard
npm install
npm start
This will automatically start the Dashboard server, open default browser and watch for source files changes.
Krane comes preconfigured for improved developer experience with Skaffold. Iterating on the project and validating the application by running the entire stack in local or remote Kubernetes cluster just got easier. Code hot-reload enables local changes to be automatically propagated to the running container for faster development lifecycle.
skaffold dev –kube-context docker-desktop –namespace krane –port-forward
Tests
Run tests locally with
bundle exec rspec












.png)


