Whonix : Privacy Protection, Anonymity Online, Anonymous Operating System
Whonix is a free and open-source desktop operating system (OS) that is specifically designed for advanced security and privacy. Based on Tor, Debian GNU/Linux and the principle of security by isolation, Whonix ™ realistically addresses common attack vectors while maintaining usability. Online anonymity and censorship circumvention is attainable via fail-safe, automatic and desktop-wide use of the Tor network, meaning...
SneakyEXE : Embedding “UAC-Bypassing” Function Into Your Custom Payload
SneakyEXE is a tool which helps you embedding UAC-Bypassing function into your custom Win32 payloads ( x86_64 architecture specifically ) Tested on Windows 7,8,10 ( 64bit)Free and Open-sourced with full source codes published Requirements LinuxWindowsArchitectureOptionalx86_64Python 3.x >YESNOModuletermcolorNODistrosAnyWindowsVersionAnyWindows 7,8,10 Also Read - Slackor : A Golang Implant That Uses Slack As A Command & Control Server Usage : This tool does require a python module called termcolor. ...
NetSet : Operational Security Utility & Automator
Operational Security utility and automator. NetSet is designed to automate a number of operations that will help the user with securing their network traffic. It also provides an easy way to gather proxies and run utilities through Tor. All the utilities installed and used by NetSet will be automatically configured as well. Of course the tool itself isn't the be all...
DarkScrape : OSINT Tool For Scraping Dark Websites
DarkScrape is a OSINT tool for scraping dark websites. OSINT tool for scraping dark websites is been testing on the following OS. Kali Linux 2019.2Ubuntu 18.04NethunterArc Linux Also Read - GoldenEye : GoldenEye Layer 7 (KeepAlive+NoCache) DoS Test Tool Installation git clone https://github.com/itsmehacker/DarkScrape.git pip3 install -r requirements.txt Features Download MediaScrape From Single UrlScraping From Files TxtCsvExcel Credit: Jake Creps Download
Ten Benefits of Writing Jobs That May Change Your Perspective
Writing is a great way to express yourself and at the same time, earn a living. When you have the right perspective about this field, you are more likely to advance further. There are numerous reasons why writing jobs are beneficial. The first obvious reason is that you can earn from it, a lot will make sense after you...
Ten Facts about Your Resume That Will Blow Your Mind
Are you looking for a job? For this, you will need a resume. In this article, we are going to give you a few hints on how to do everything properly. A resume is the first requirement that comes to mind when looking for a job. It is a chance to showcase yourself. However, there are some hidden facts...
Youzer : Fake User Generator For Active Directory Environments
Fake User Generator for Active Directory Environments. The goal of Youzer is to create information rich Active Directory environments. This uses the python3 library 'faker' to generate random accounts. pip3 install faker You can either supply a wordlist or have the passwords generated. The generated option is great for testing things like hashcat rule masks. Wordlist option is useful...
Rock-ON : All In One Recon Tool That Will Just Get A Single Entry Of The Domain Name & Do All Of The Work Alone
Rock-On is a all in one recon tool that will help your Recon process give a boost. It is mainly aimed to automate the whole process of recon and save the time that is being wasted in doing all this stuffs manually. A thorough blog will be up in sometime. Stay tuned for the Stable...
FBChecker : Facebook Mass Account Checker
FBChecker is a tool that is used for a Facebook mass account checker.Facebook Mass Account Checker Simple Installation : apt install gitapt install phpgit clone https://github.com/fdciabdul/fbcheckercd fbcheckerphp fbcheck.php Also Read - MIG : Distributed & Real Time Digital Forensics At The Speed Of The Cloud Usage php fbcheck.php target.txt Download
WESNG : Next Generation Windows Exploit Suggester
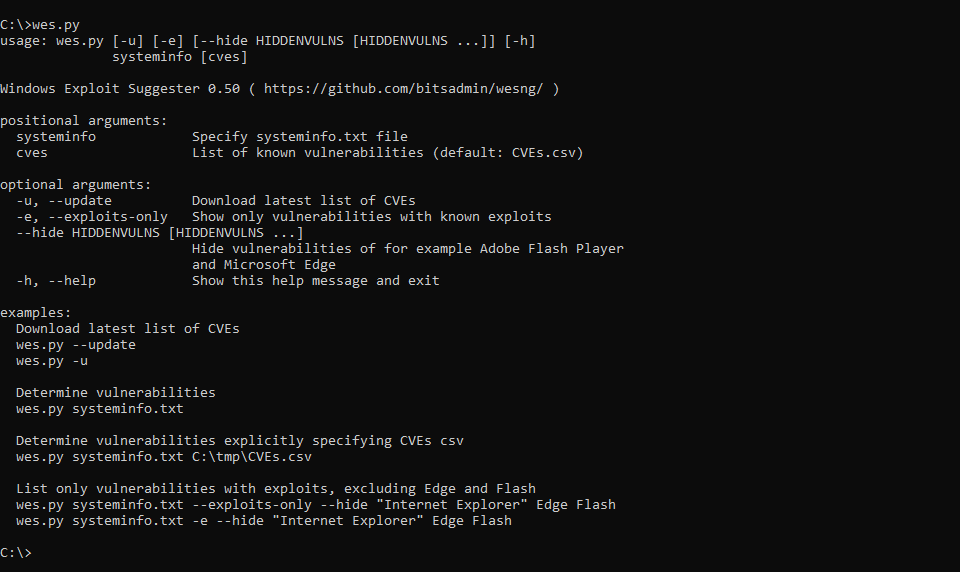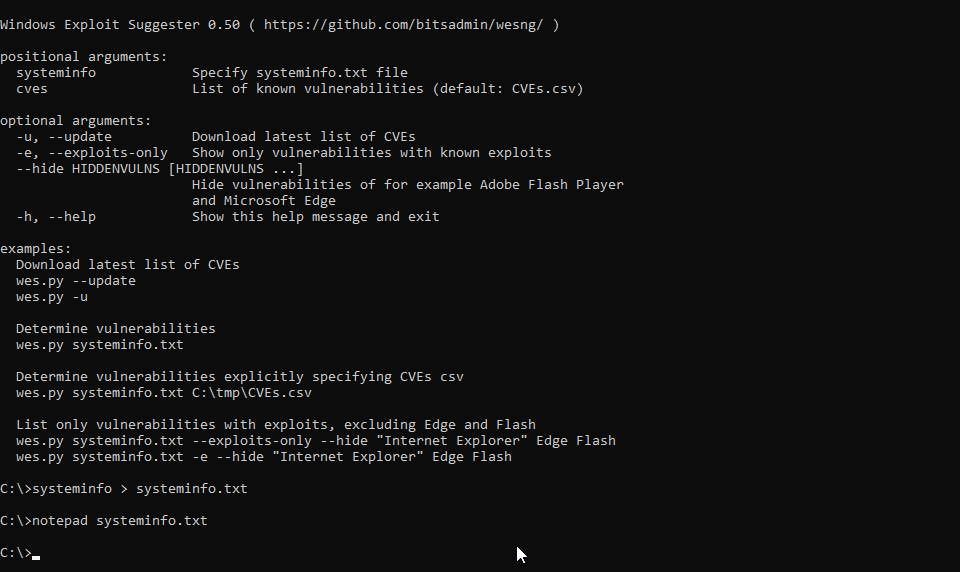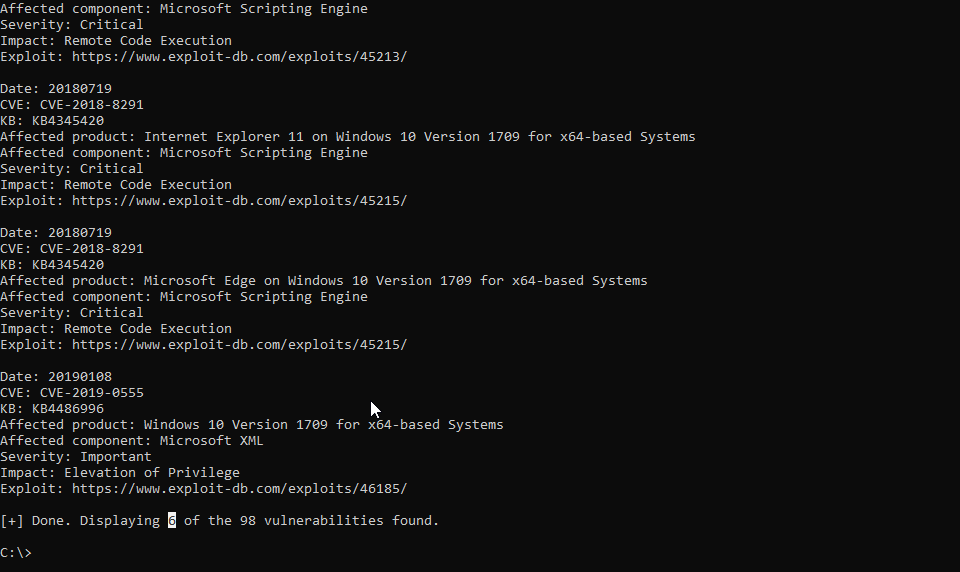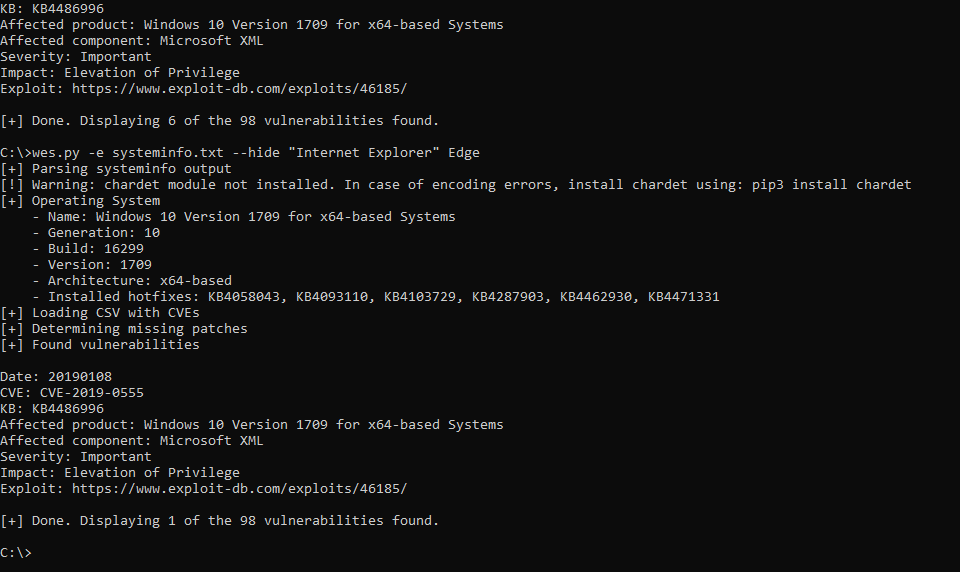
WESNG is a tool based on the output of Windows' systeminfo utility which provides the list of vulnerabilities the OS is vulnerable to, including any exploits for these vulnerabilities. Every Windows OS between Windows XP and Windows 10, including their Windows Server counterparts, is supported. Usage Obtain the latest database of vulnerabilities by executing the command wes.py...