Memhunter is an endpoint sensor tool that is specialized in detecing resident malware, improving the threat hunter analysis process and remediation times. The tool detects and reports memory-resident malware living on endpoint processes. Memhunter detects known malicious memory injection techniques. The detection process is performed through live analysis and without needing memory dumps.
The tool was designed as a replacement of memory forensic volatility plugins such as malfind and hollowfind. The idea of not requiring memory dumps helps on performing the memory resident malware threat hunting at scale, without manual analysis, and without the complex infrastructure needed to move dumps to forensic environments.
The detection process is performed through a combination of endpoint data collection and memory inspection scanners. The tool is a standalone binary that, upon execution, deploys itself as a windows service. Once running as a service, memhunter starts the collection of ETW events that might indicate code injection attacks.
The live stream of collected data events is feed into memory inspection scanners that use detection heuristics to down select the potential attacks. The entire detection process does not require human intervention, neither memory dumps, and it can be performed by the tool itself at scale.
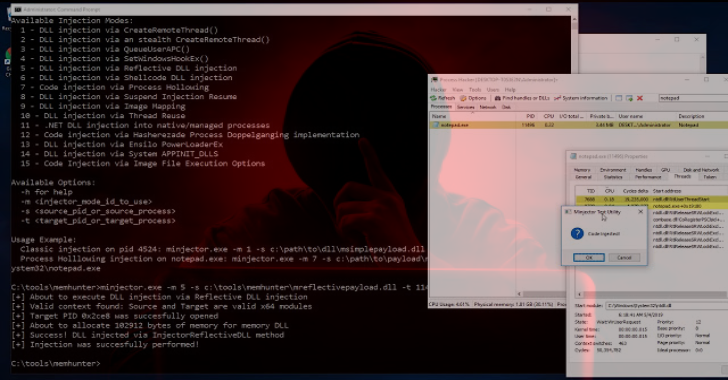
Besides the data collection and hunting heuristics, the project has also led to the creation of a companion tool called “minjector” that contains +15 code injection techniques. The minjector tool cannot onlybe used to exercise memhunter detections, but also as a one-stop location to learn on well-known code injection techniques out there.
Also Read – KsDumper : Dumping Processes Using The Power Of Kernel Space
Example 1: Manual run to exercise detection of reflective DLL injection
Example 2: Manual run to exercise detection of process hollowing injection