Project Black is a scope control, scope scanner and progress tracker for easier working on a bug bounty or pentest project. The tools encourages more methodical work on pentest/bugbounty, tracking the progress and general scans information.
It can launch
- masscan
- nmap
- dirsearch
- amass
- patator
against the scope you work on and store the data in a handy form. Perform useful filtering of the project’s data, for instance:
- find me all hosts, which have open ports, but not 80
- find me all hosts, whose ips start with 82.
- find me hosts where dirsearch has found at least 1 file with 200 status code
Installation
Basic setup via docker-compose will run on any system which has docker and docker-compose dependency
Also Read – Application Inspector : A Source Code Analyzer Built For Surfacing Features Of Interest
If you don’t have docker installed then
Docker for Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt install docker.io
Tool Installation
If you have docker set up, then for Ubuntu/Debian simply
-sudo curl -L “https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.23.1/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)” -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
-sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
-git clone https://github.com/c0rvax/project-black
-cd project-black
-sudo docker-compose up
If you see some SQL errors, try stopping docker-compose (Ctrl + C once and wait for nice shutdown) and run docker-compose up
This might take some time but that’s it! Other distros should have very similar guidance.
Now head to http://localhost:5000, enter the credentials. They can be found in https://github.com/c0rvax/project-black/blob/master/config/config_docker.yml under application
For a more complex setup or something failed, see the wiki.
Resources Notice
None of the docker containers restrict the amount of resources usage, you are on your own here, however, you can change the amount of parallel tasks for each worker separately. See the wiki for that
How to work?
After a setup, create a project and head to the respective page.
Now we will follow the basic steps which you can do within the application
Add scope
Let’s say we are assessing hackerone.com and all it’s subdomains. Write hackerone.com into the add scope field and press Add to scope
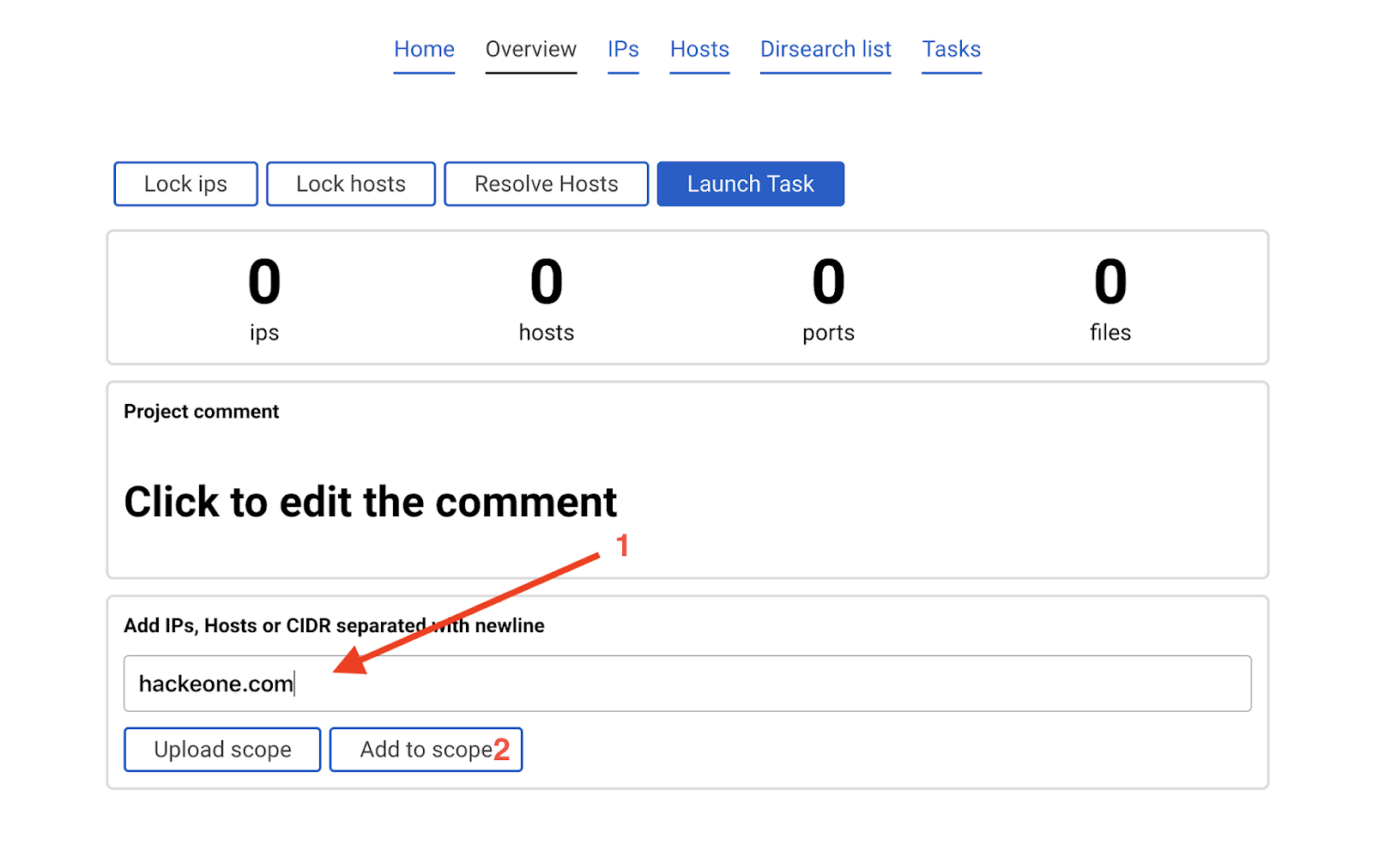
Entrypoint has been added.
There are other ways to add scope, see wiki
Quick note on working
All of the tasks can read parameters from the user, however, lauching with some options won’t diplay any new result as it is pretty difficult to parse all possible outputs of a program. So to start, try working duplicating the options from this manual.
Available options can be found on this page
Start amass
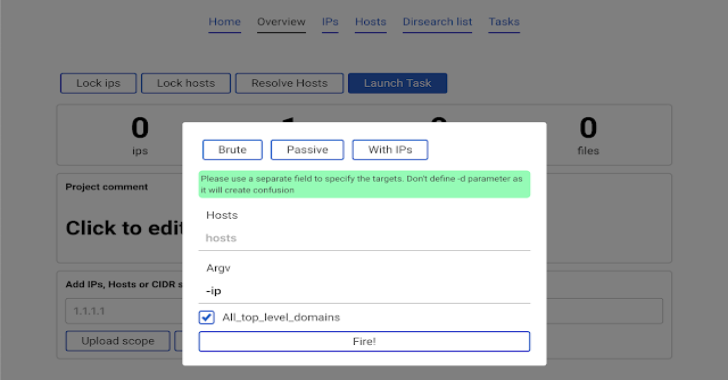
Click the blue button Launch task.
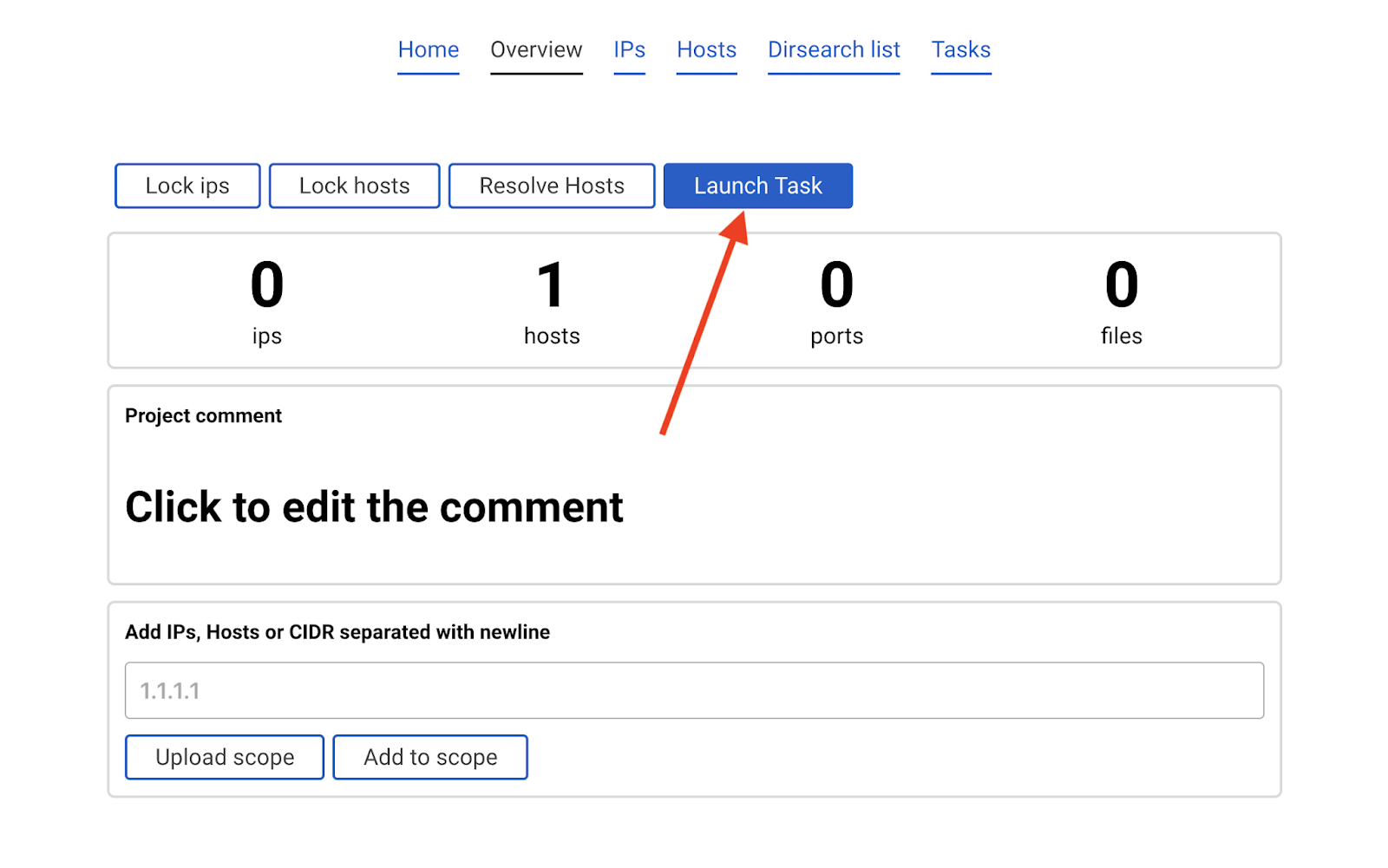
A popup with parameters will appear.
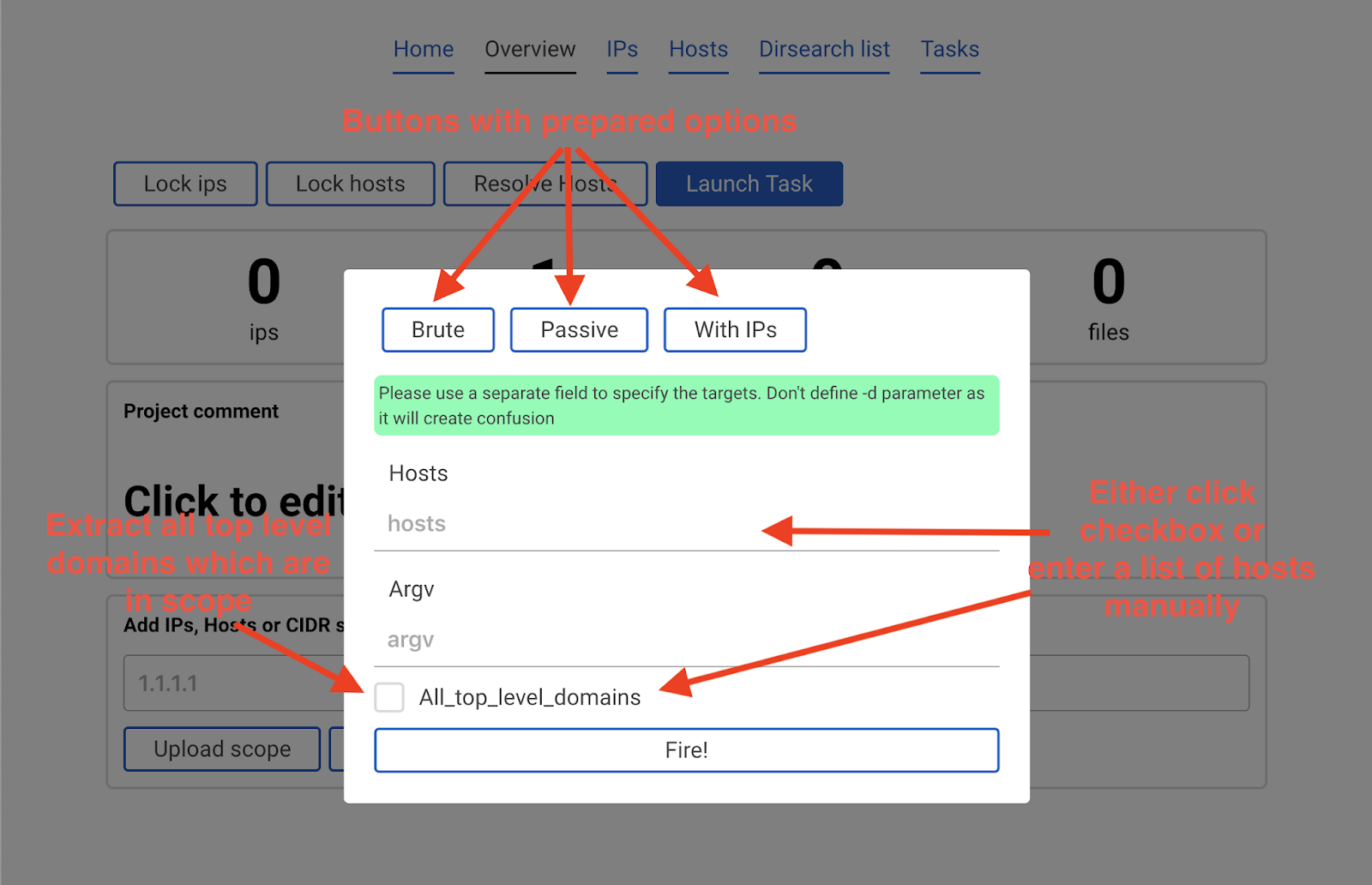
It is recommended to click the All_top_level_domains check box and in argv enter -ip and click Fire! button.
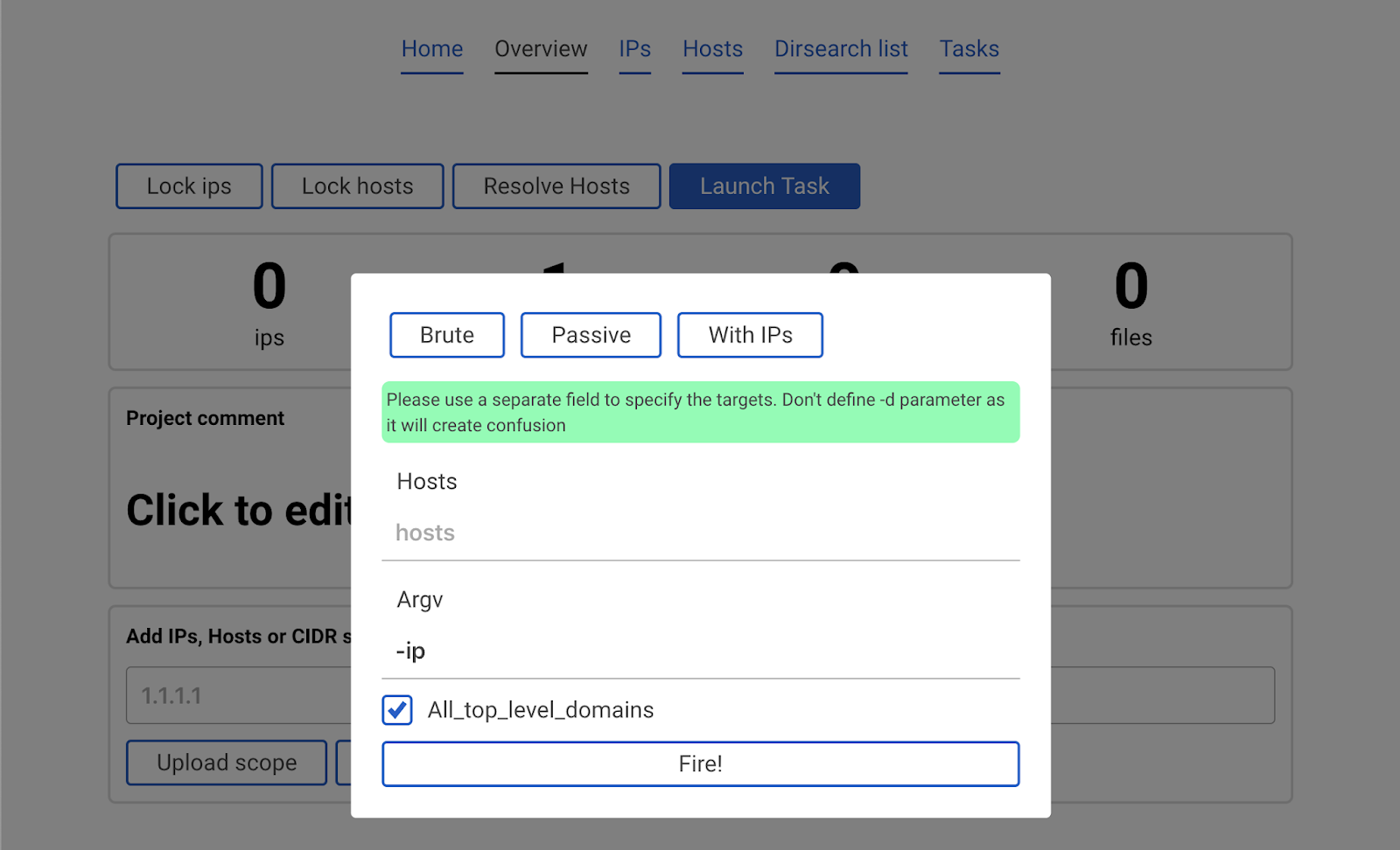
This would launch amass -d hackerone.com -ip. Note that in this case we did not specify any domain. This is beacause the All_top_level_domains check box means looking into the scope which is stored in the database. So the program sees that hackerone.com was added to the scope and launches amass against it.
Upon finishing, the new data is automatically added to scope.
Start masscan and nmap
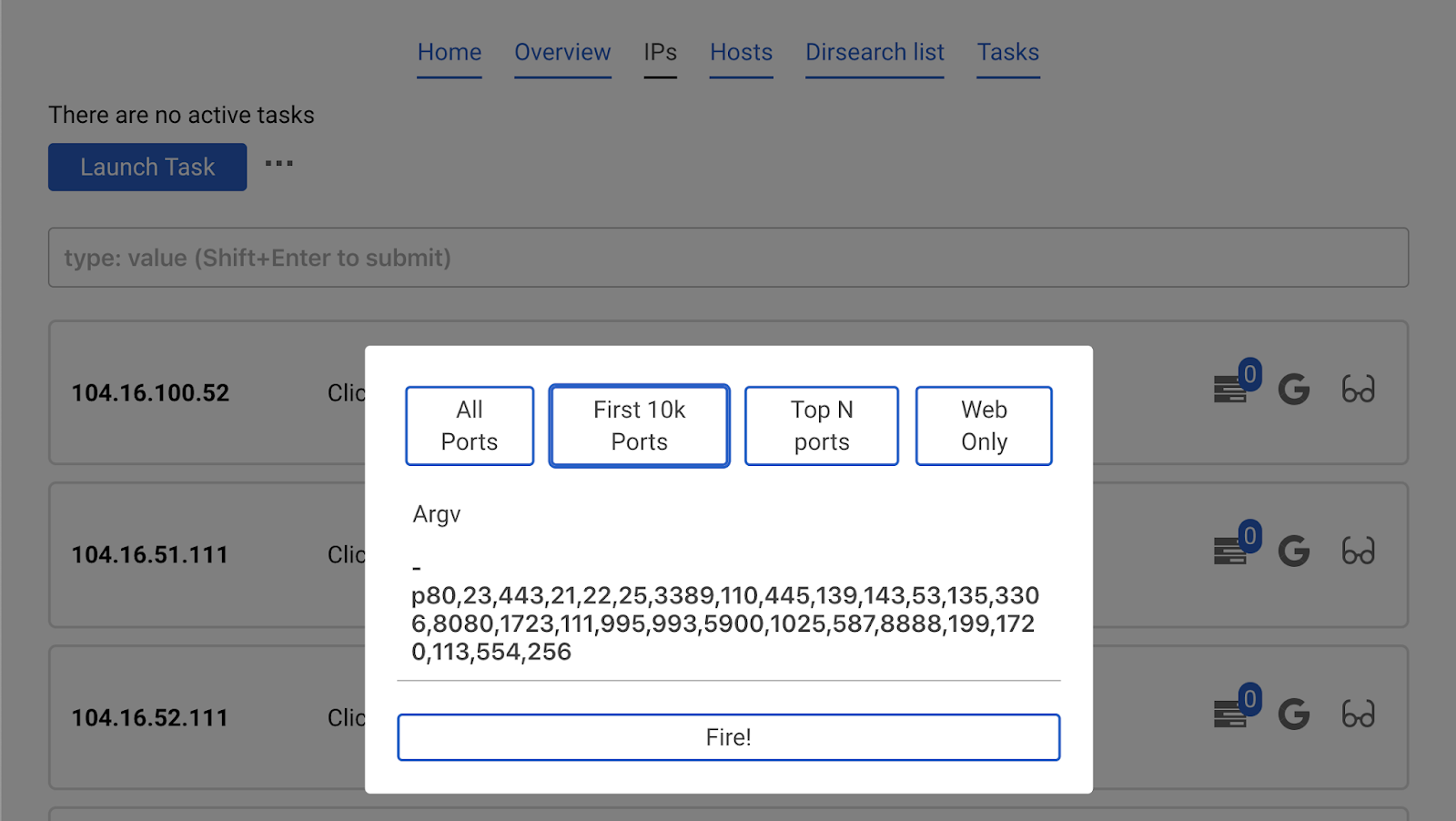
Now head to IPs tab. Click the already known button Launch task and choose masscan.
We will launch a quick scan, using the button Top N ports. This autocompletes the argv parameter. Press Fire!
Results are automatically downloaded from the database.
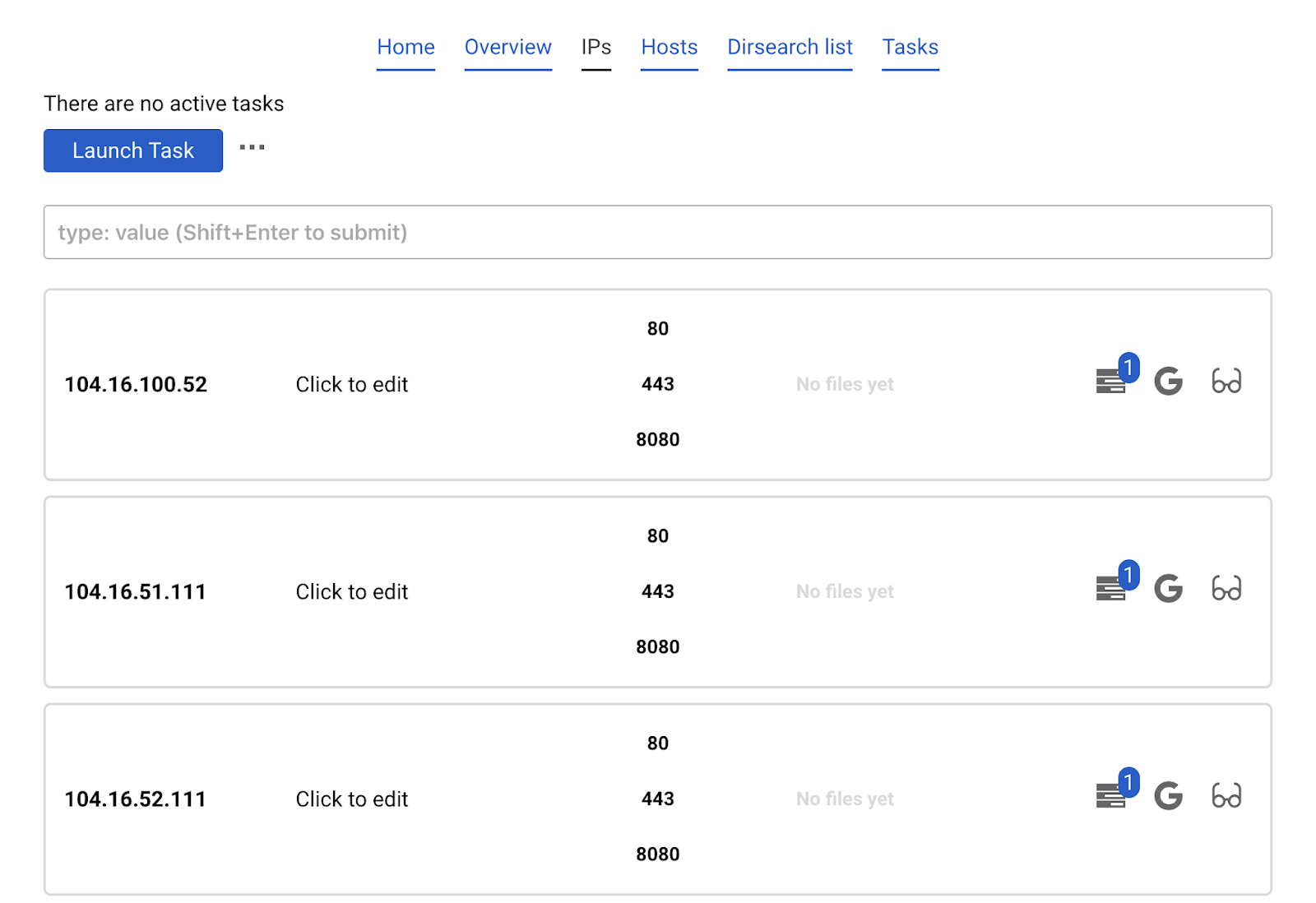
Now click Launch task and choose nmap only open. This will find all the open ports which exist in the database and run nmap only against them.
Click Banner and Fire.
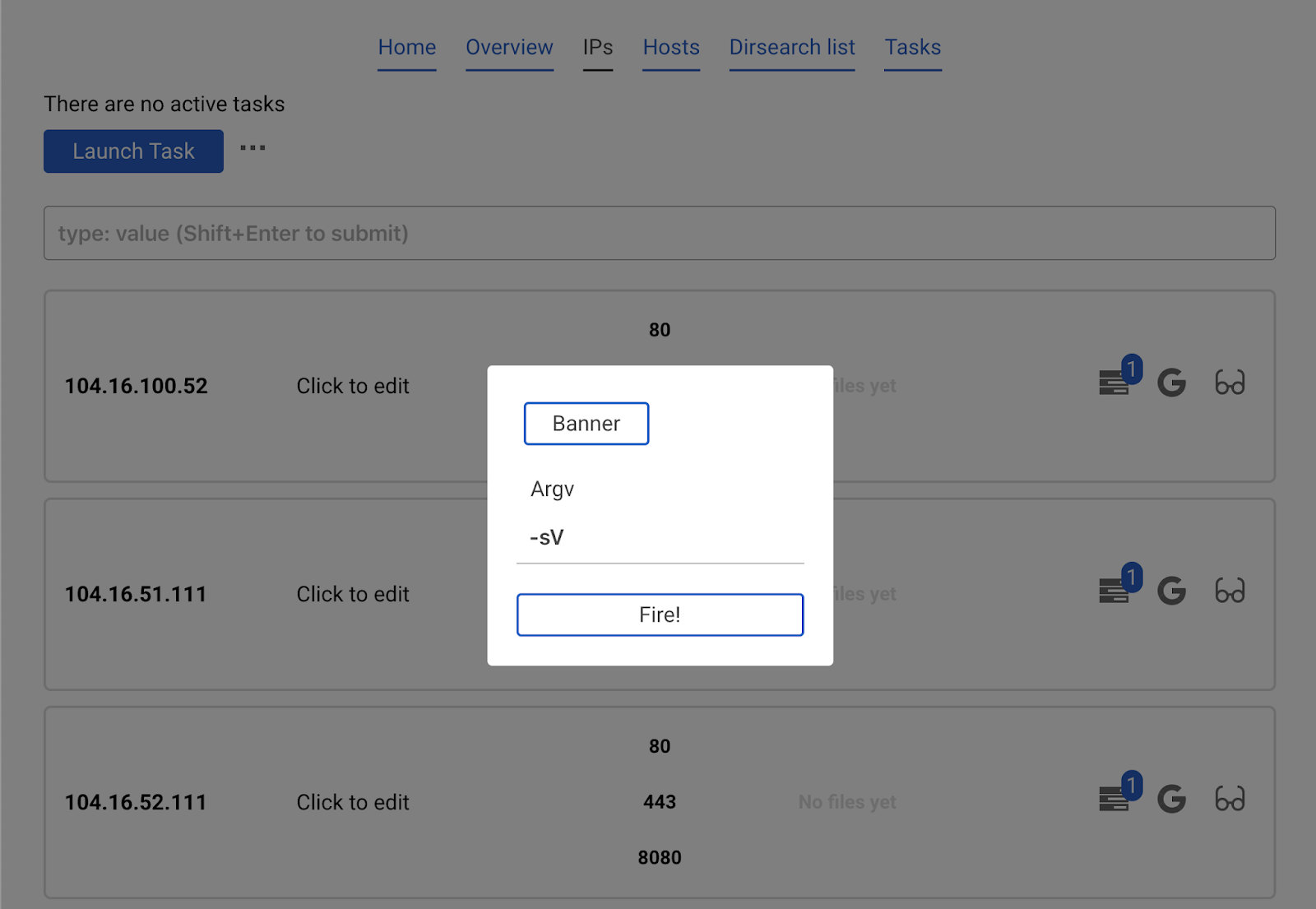
Detected banner will automatically appear
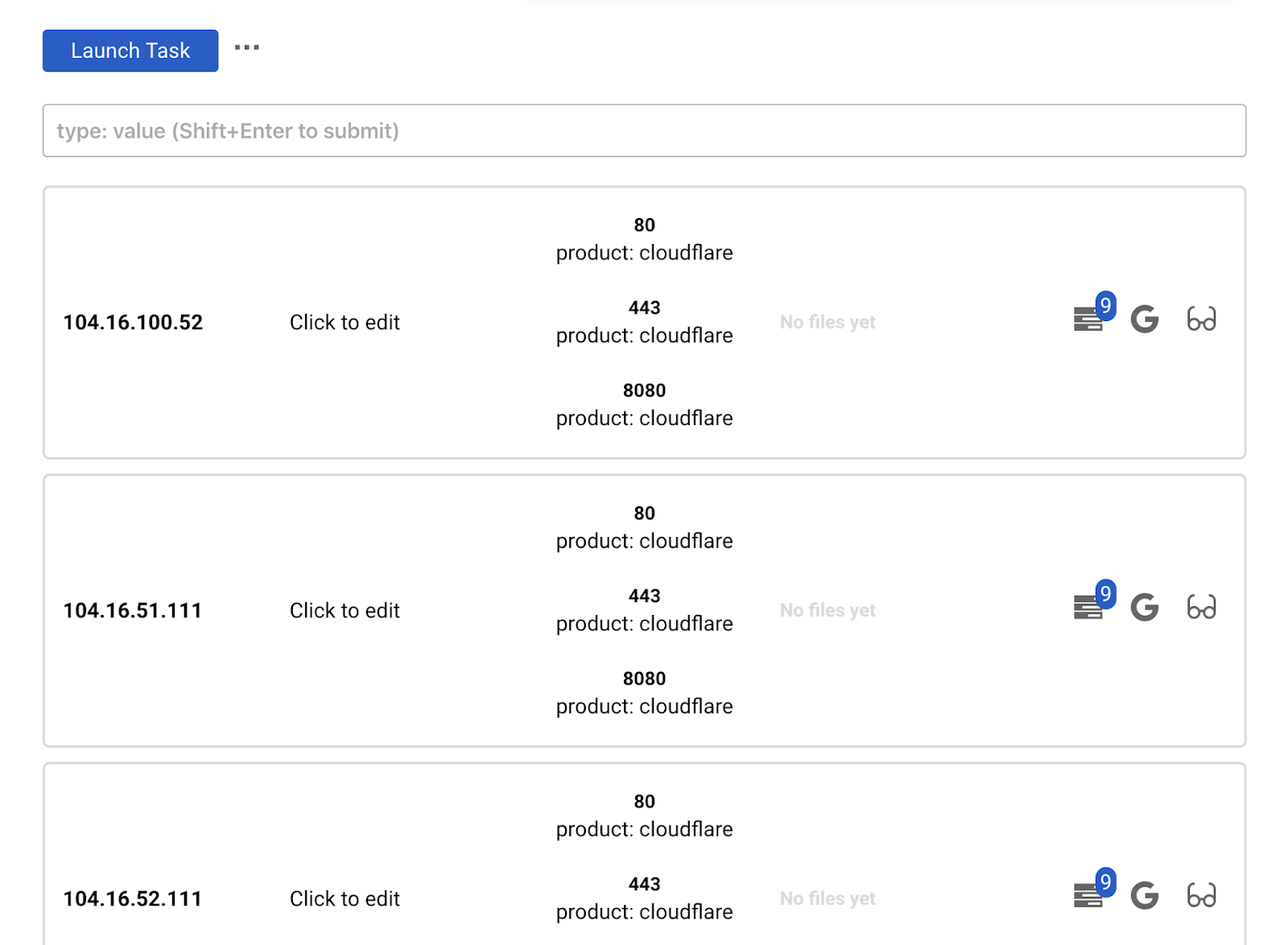
Launching dirsearch
Launch dirsearch against all ips and all open ports (both HTTP and HTTPS would be tried)
On IPs tab click Launch task and select dirsearch. Fill in extenstions you want to try and click Fire!
You can launch dirseach agains hosts (not ips) on the Hosts tab.
Note on dirsearch
If there are no ports, dirsearch won’t even start. So first, make sure you launched nmap or masscan to discover open ports.
Inspecting results
There are generally three ways to check the results:
- IPs/Hosts list
- IP/Host details
- Dirsearch list
IPs and Hosts list
Those are two tabs. They work the same way so we will stop on Hosts.
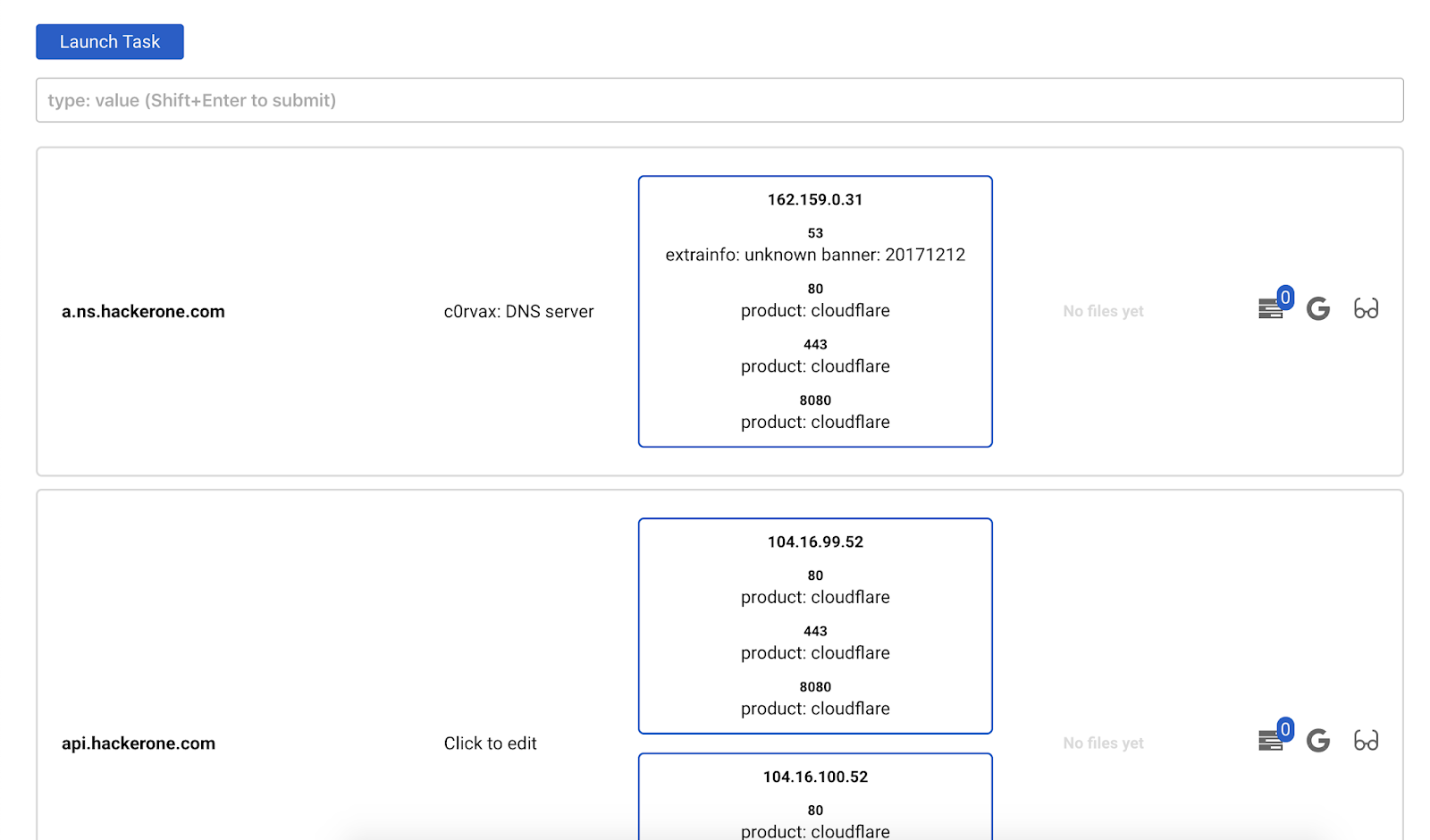
You can see a list of hosts, their ports and files. Also you can edit a comment for that host.
Important part here is filtering box.

You can aggregate different filters using the field shown above. Type the filter you want (there is a helper for that) and press Shift + Enter

IP/Host details
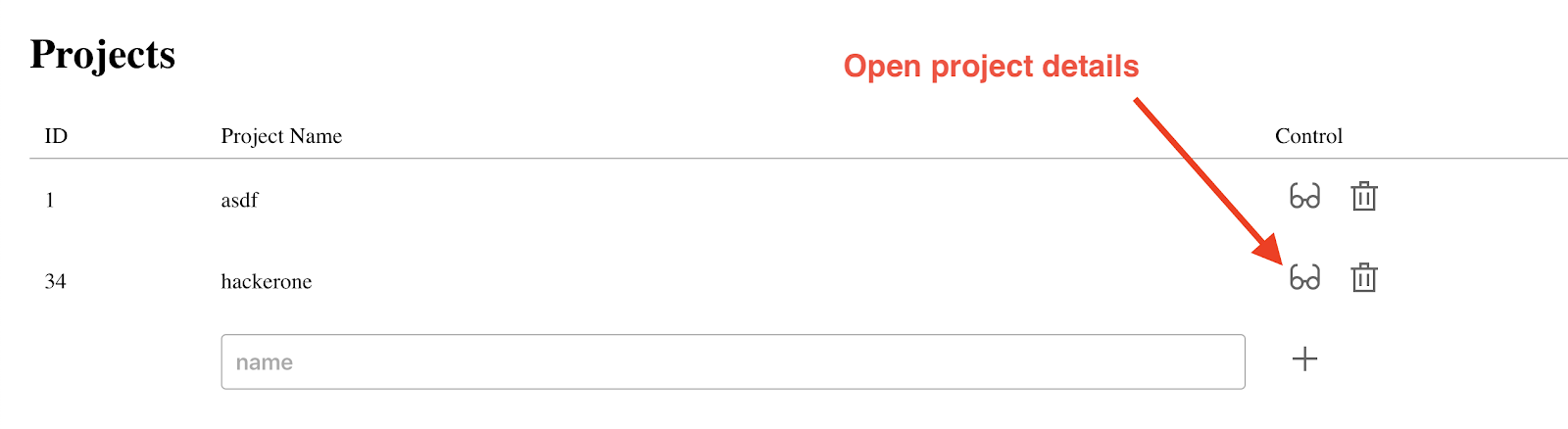
You can also view details on a specific host or ip. Press button with the glasses
There you will see dirsearch result for every open port on that host
Dirsearch list
Dirsearch list button will open a new window showing all found files for every dirsearch which was launched in this project.
Launching tasks against specific scope
IPs and Hosts Launch task are different! The button on IPs page will start against all ips within the current project, meanwhile the button on the Hosts page will launch against hosts.
To launch a task against some hosts, you should
- Filter the hosts
- Launch the task
Example:
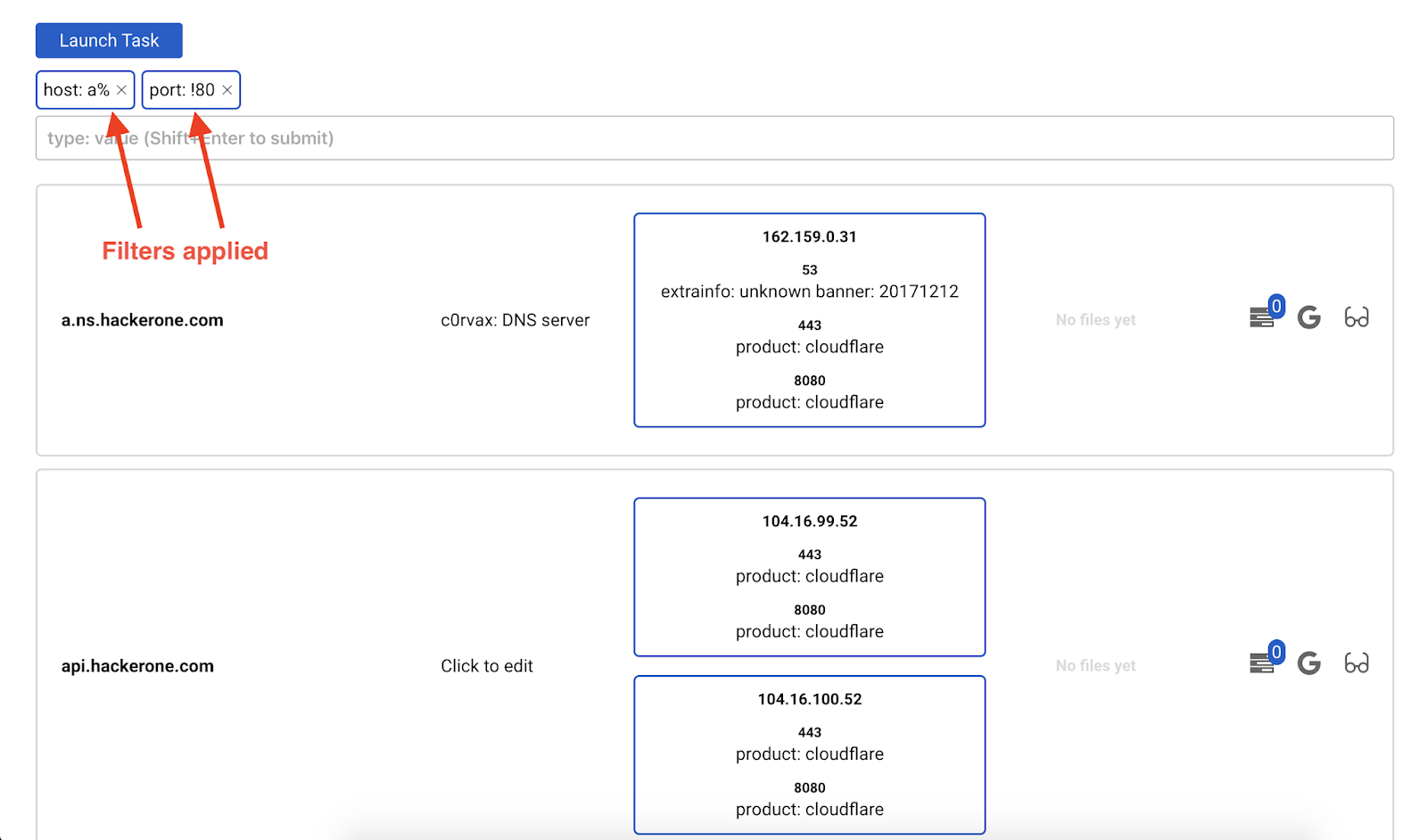
Some filters have been applied. If we now launch dirsearch, it will be launched against hosts which correspond to the used filters.














.png)
.png)
