FaPro is a Fake Protocol Server tool, Can easily start or stop multiple network services.
The goal is to support as many protocols as possible, and support as many deep interactions as possible for each protocol.
Demo Site
- Supported Running Modes:
- Local Machine
- Virtual Network
- Supported Protocols:
- DNS
- DCE/RPC
- EIP
- Elasticsearch
- FTP
- HTTP
- IEC 104
- Memcached
- Modbus
- MQTT
- MySQL
- RDP
- Redis
- S7
- SMB
- SMTP
- SNMP
- SSH
- Telnet
- VNC
- IMAP
- POP3
- NTP
- RTSP
- PORTMAP
- Use TcpForward to forward network traffic
- Support tcp syn logging
- Support icmp ping logging
- Support udp packet logging
Support credssp ntlmv2 nla authentication.
Support to configure the image displayed when user login.
SSH
Support user login.
Support fake terminal commands, such as id, uid, whoami, etc.
Account format: username:password:home:uid

IMAP & SMTP
Support user login and interaction.
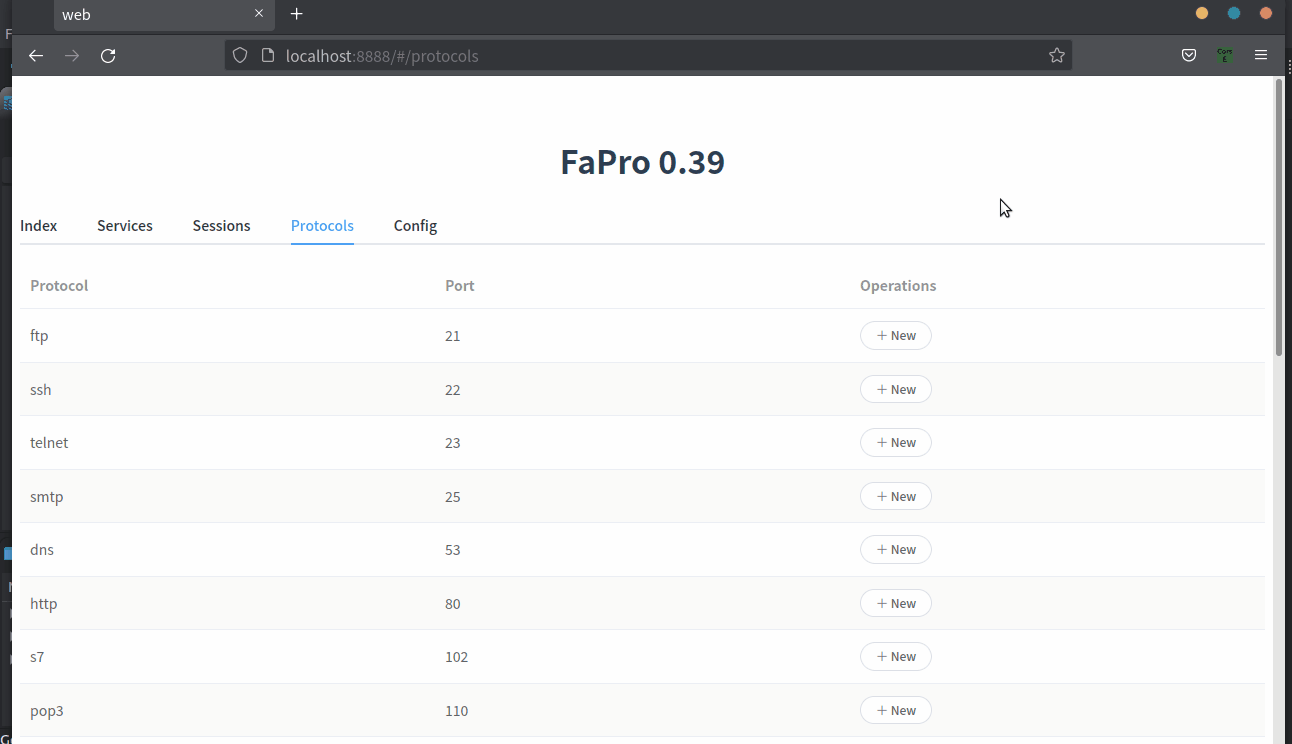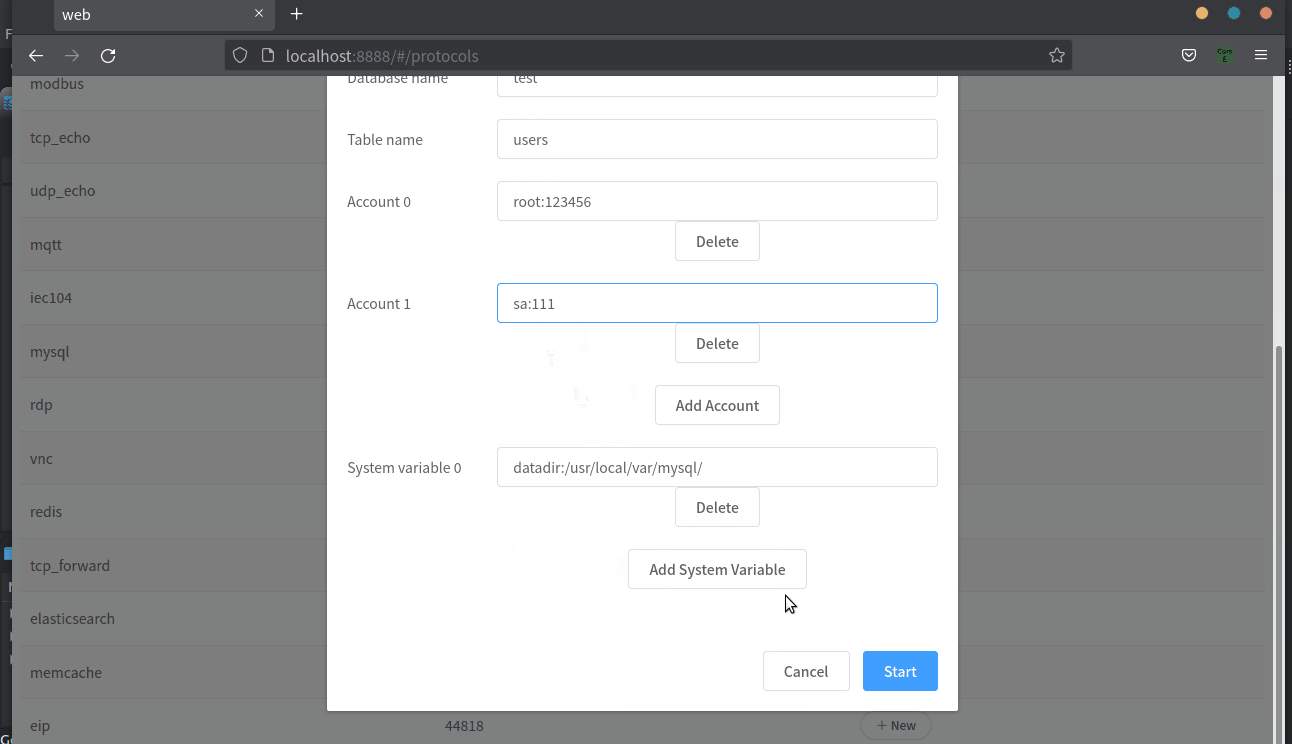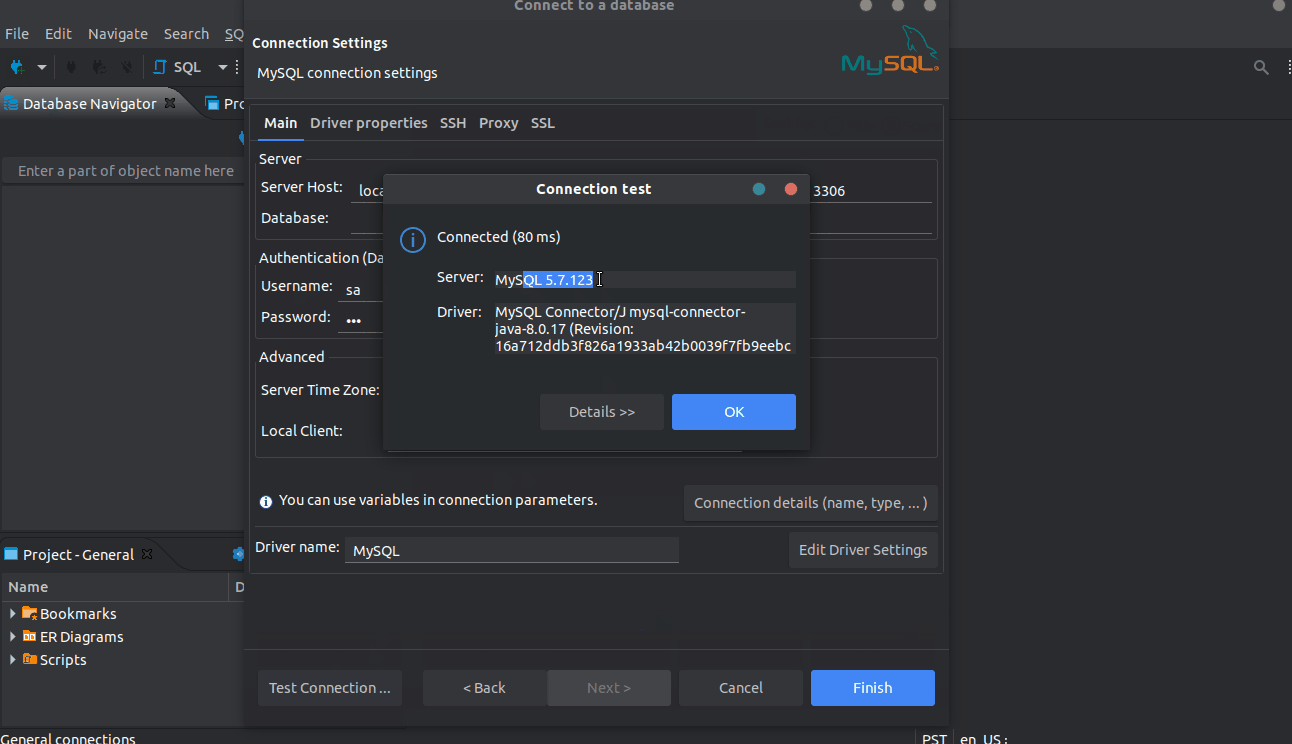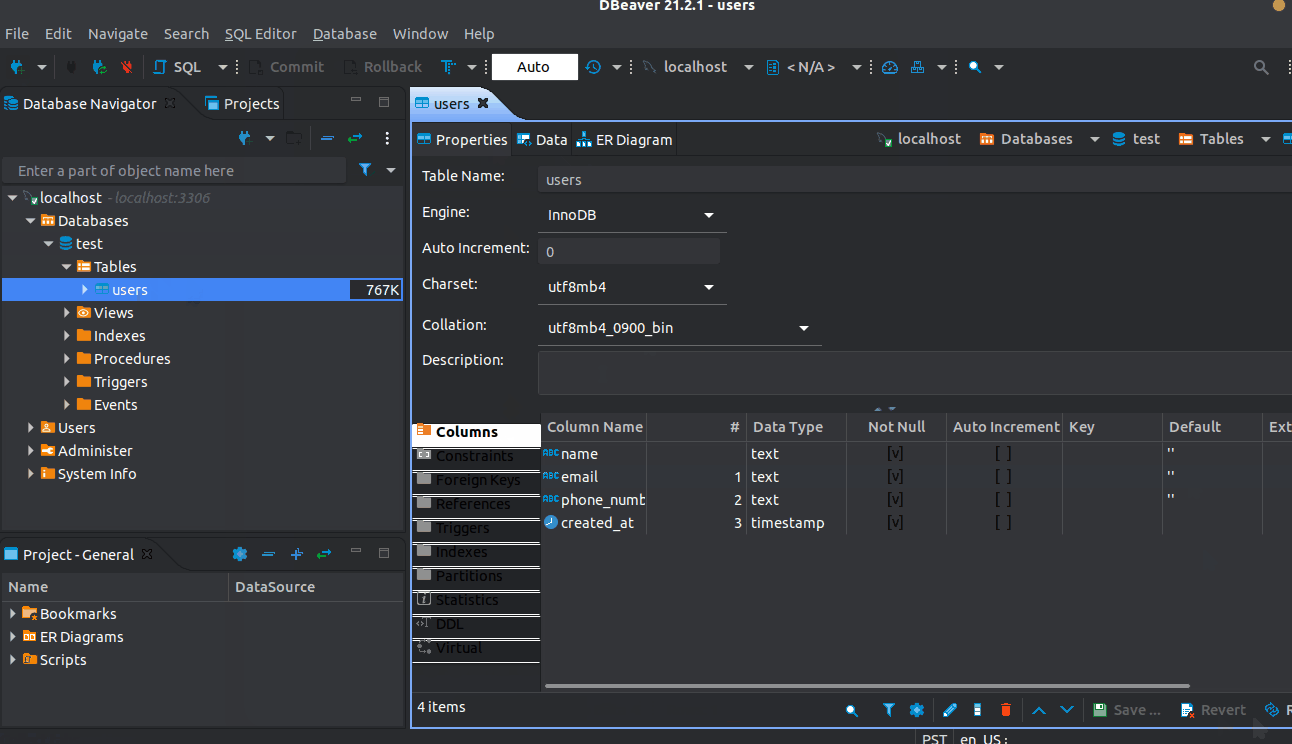
Mysql
Support sql statement query interaction
HTTP
Support website clone, You need to install the chrome browser and chrome driver to work.
The configuration of all protocols and parameters is generated by genConfig subcommand.
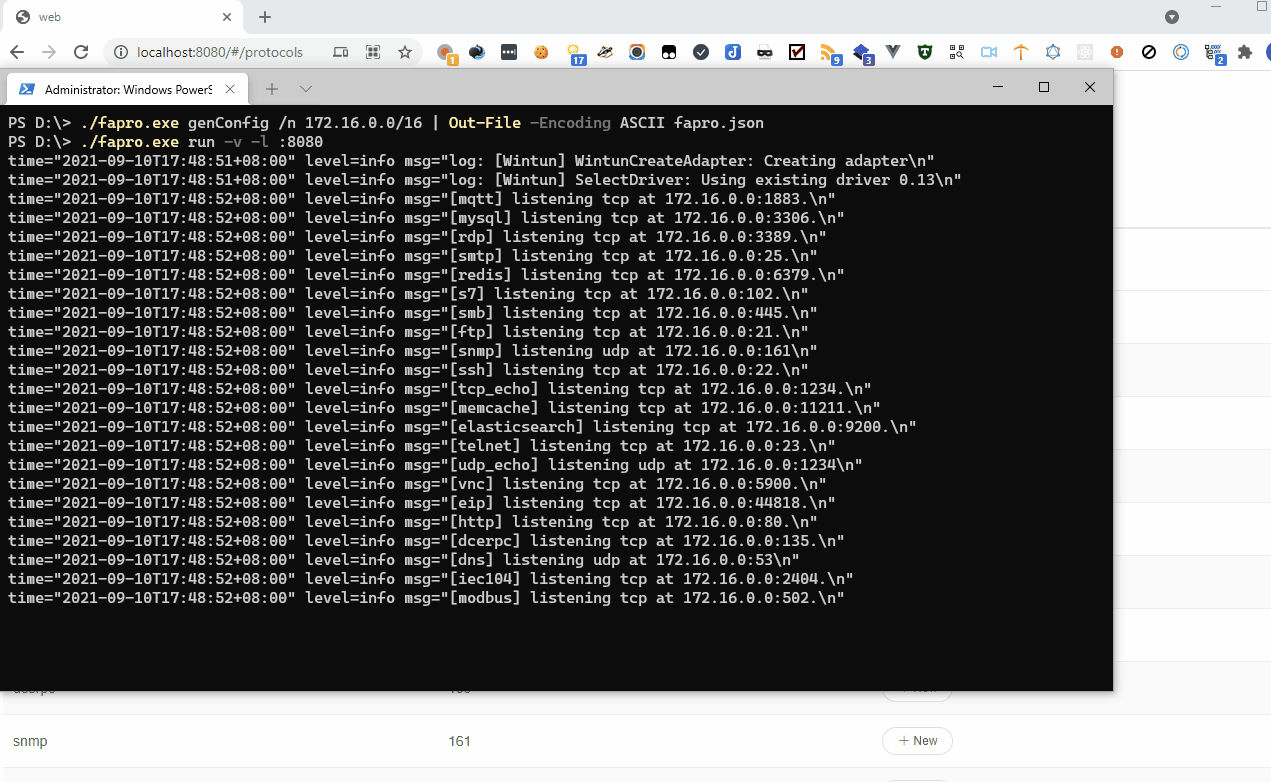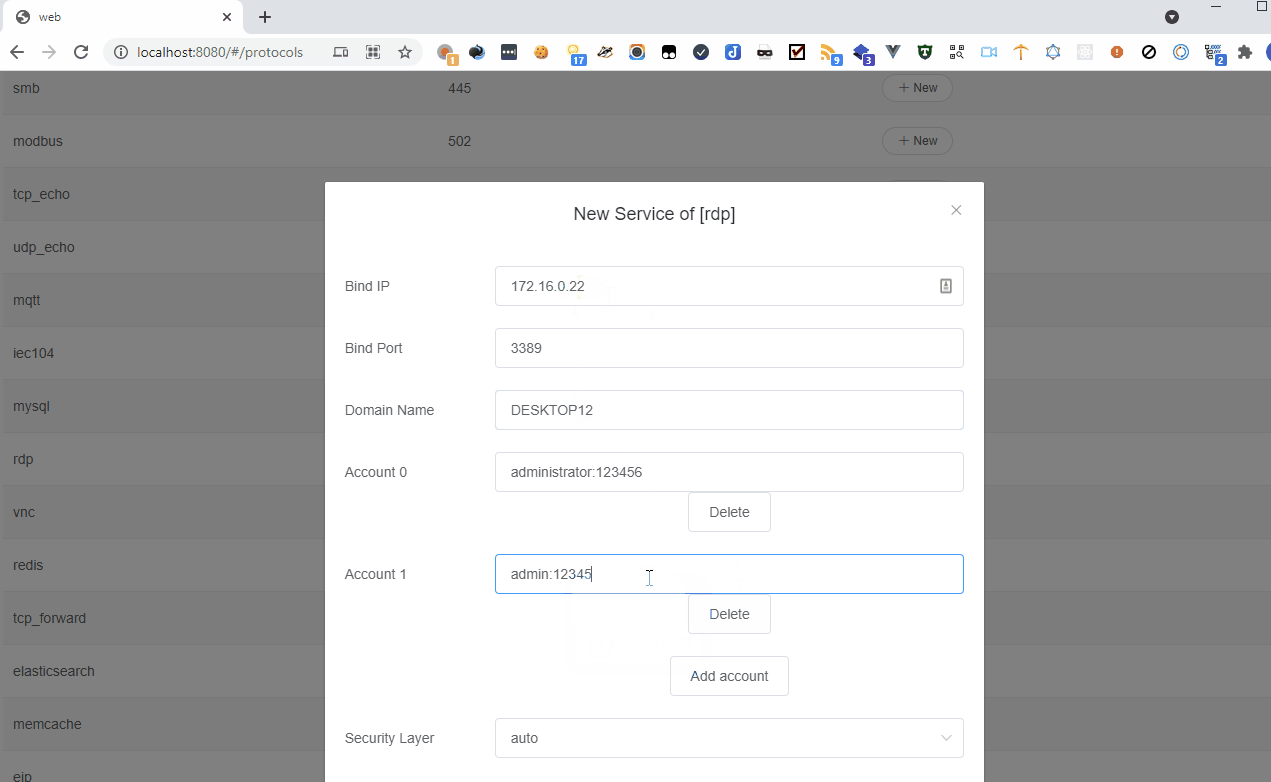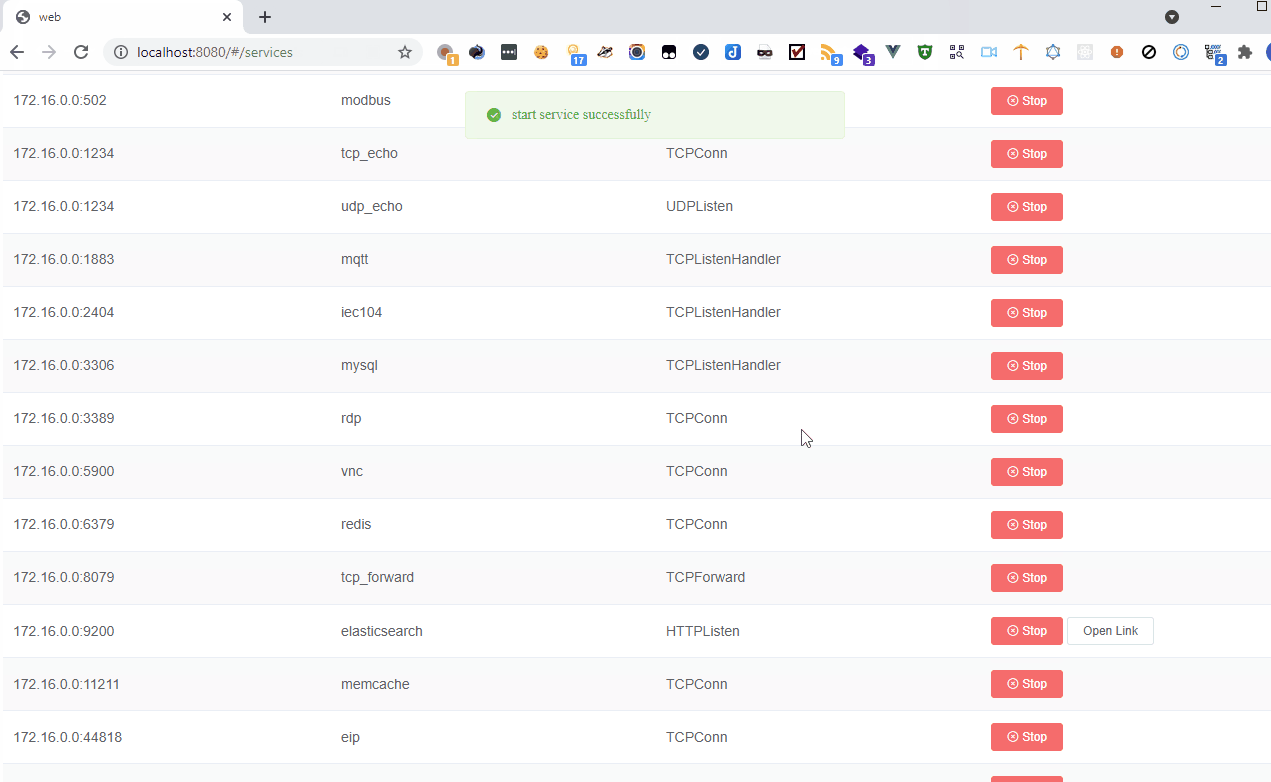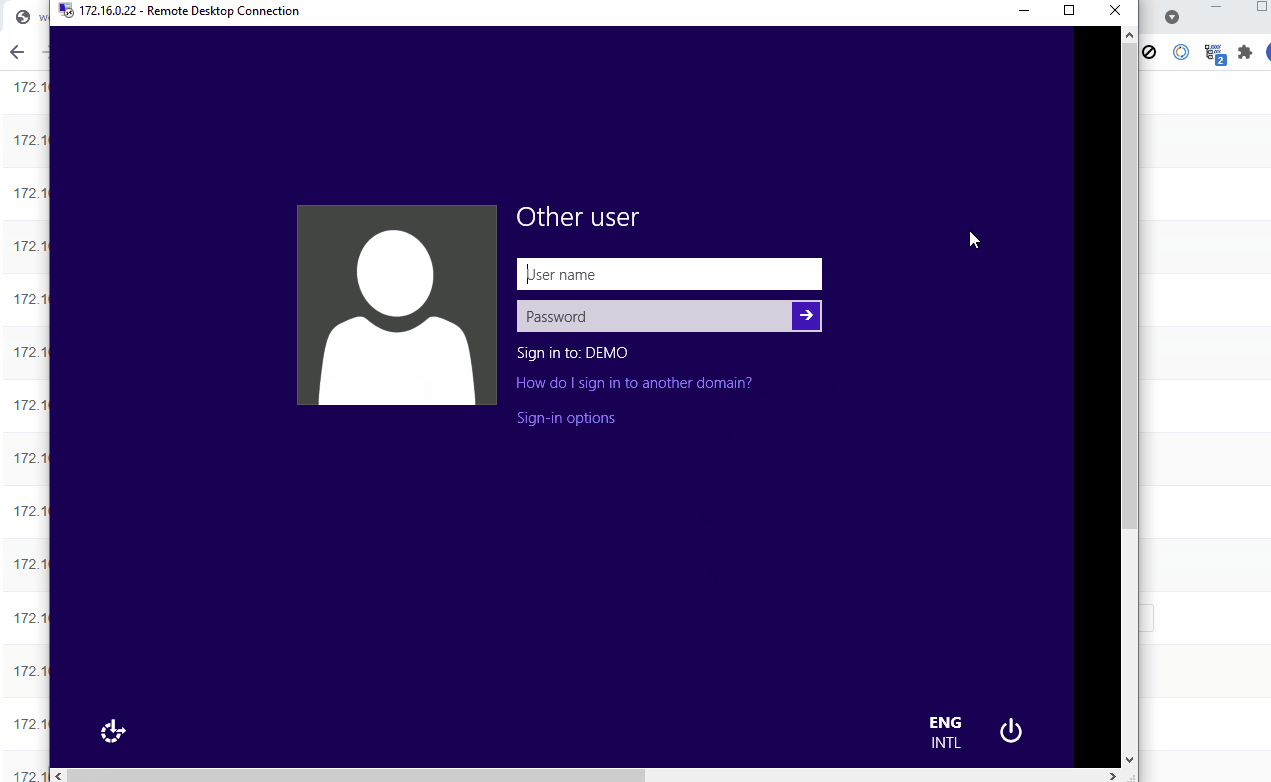
Use 172.16.0.0/16 subnet to generate the configuration file:
fapro genConfig -n 172.16.0.0/16 > fapro.json
Or use local address instead of the virtual network:
fapro genConfig > fapro.json
Run the protocol simulator
Run FaPro in verbose mode and start the web service on port 8080:
fapro run -v -l :8080
Tcp syn logging
For windows users, please install winpcap or npcap.
Use ELK to analyze protocol logs:

Configuration
This section contains the sample configuration used by FaPro.
{
“version”: “0.40”,
“network”: “127.0.0.1/32”,
“network_build”: “localhost”,
“storage”: null,
“geo_db”: “/tmp/geoip_city.mmdb”,
“hostname”: “fapro1”,
“use_logq”: true,
“cert_name”: “unknown”,
“syn_dev”: “any”,
“udp_dev”: “any”,
“icmp_dev”: “any”,
“exclusions”: [],
“hosts”: [
{
“ip”: “127.0.0.1”,
“handlers”: [
{
“handler”: “dcerpc”,
“port”: 135,
“params”: {
“accounts”: [
“administrator:123456”,
],
“domain_name”: “DESKTOP-Q1Test”
}
}
]
}
]
}
- version: Configuration version.
- network: The subnet used by the virtual network or the address bound to the local machine(Local mode).
- network_build: Network mode(supported value: localhost, all, userdef)
- localhost: Local mode, all services are listening on the local machine
- all: Create all hosts in the subnet(i.e., Can ping all the host in the subnet)
- userdef: Create only the hosts specified in the hosts configuration.
- storage: Specify the storage used for log collection, support sqlite, mysql, elasticsearch. e.g.
- sqlite3:logs.db
- mysql://user:password@tcp(127.0.0.1:3306)/logs
- es://http://username:password@127.0.0.1:9200 (currently only supports Elasticsearch 7.x)
- geo_db: MaxMind geoip2 database file path, used to generate ip geographic location information. if you use Elasticsearch storage, never need this field, it will be automatically generated using the geoip processor of Elasticsearch.
- hostname: Specify the host field in the log.
- use_logq: Use local disk message queue to save logs, and then send it to remote mysql or Elasticsearch to prevent remote log loss.
- cert_name: Common name of the generated certificate.
- syn_dev: Specify the network interface used to capture tcp syn packets. If it is empty, the tcp syn packet will not be recorded. On windows, the device name is like “\Device\NPF_{xxxx-xxxx}”.
- udp_dev: Same as syn_dev, but for udp packet.
- icmp_dev: Same as syn_dev, but for icmp ping packet.
- exclusions: Exclude remote ips from logs.
- hosts: Each item is a host configuration.
- handlers: Service configuration, the service configured on the host, each item is a service configuration.
- handler: Service name (i.e., protocol name)
- params: Set the parameters supported by the service.
Create a virtual network, The subnet is 172.16.0.0/24, include 2 hosts,
172.16.0.3 run dns, ssh service,
and 172.16.0.5 run rpc, rdp service,
protocol access logs are saved to elasticsearch, exclude the access log of 127.0.0.1 and 8.8.8.8.
{
“version”: “0.40”,
“network”: “172.16.0.0/24”,
“network_build”: “userdef”,
“storage”: “es://http://127.0.0.1:9200”,
“use_logq”: true,
“cert_name”: “unknown”,
“syn_dev”: “any”,
“udp_dev”: “any”,
“icmp_dev”: “any”,
“exclusions”: [“127.0.0.1”, “8.8.8.8”],
“geo_db”: “”,
“hosts”: [
{
“ip”: “172.16.0.3”,
“handlers”: [
{
“handler”: “dns”,
“port”: 53,
“params”: {
“accounts”: [
“admin:123456”
],
“appname”: “domain”
}
},
{
“handler”: “ssh”,
“port”: 22,
“params”: {
“accounts”: [
“root:5555555:/root:0”
],
“prompt”: “$ “,
“server_version”: “SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_7.4”
}
}
]
},
{
“ip”: “172.16.0.5”,
“handlers”: [
{
“handler”: “dcerpc”,
“port”: 135,
“params”: {
“accounts”: [
“administrator:123456”
],
“domain_name”: “DESKTOP-Q1Test”
}
},
{
“handler”: “rdp”,
“port”: 3389,
“params”: {
“accounts”: [
“administrator:123456”
],
“auth”: false,
“domain_name”: “DESKTOP-Q1Test”,
“image”: “rdp.jpg”,
“sec_layer”: “auto”
}
}
]
}
]
}
Automatically generate service configuration
Use the ipclone.py script in Scripts, You can clone the ip service configuration from fofa to quickly generate the service configuration of the real machine.