A utility for playing with cryptography, geared towards ransomware analysis. CryptoTester is a powerful utility designed for in-depth cryptographic analysis, with a particular focus on ransomware investigation.
In this article, we’ll explore how CryptoTester provides a robust set of tools and features to aid in dissecting and understanding cryptographic elements, making it an invaluable asset for cybersecurity experts and researchers dealing with ransomware threats.
A utility for playing with cryptography, geared towards ransomware analysis.
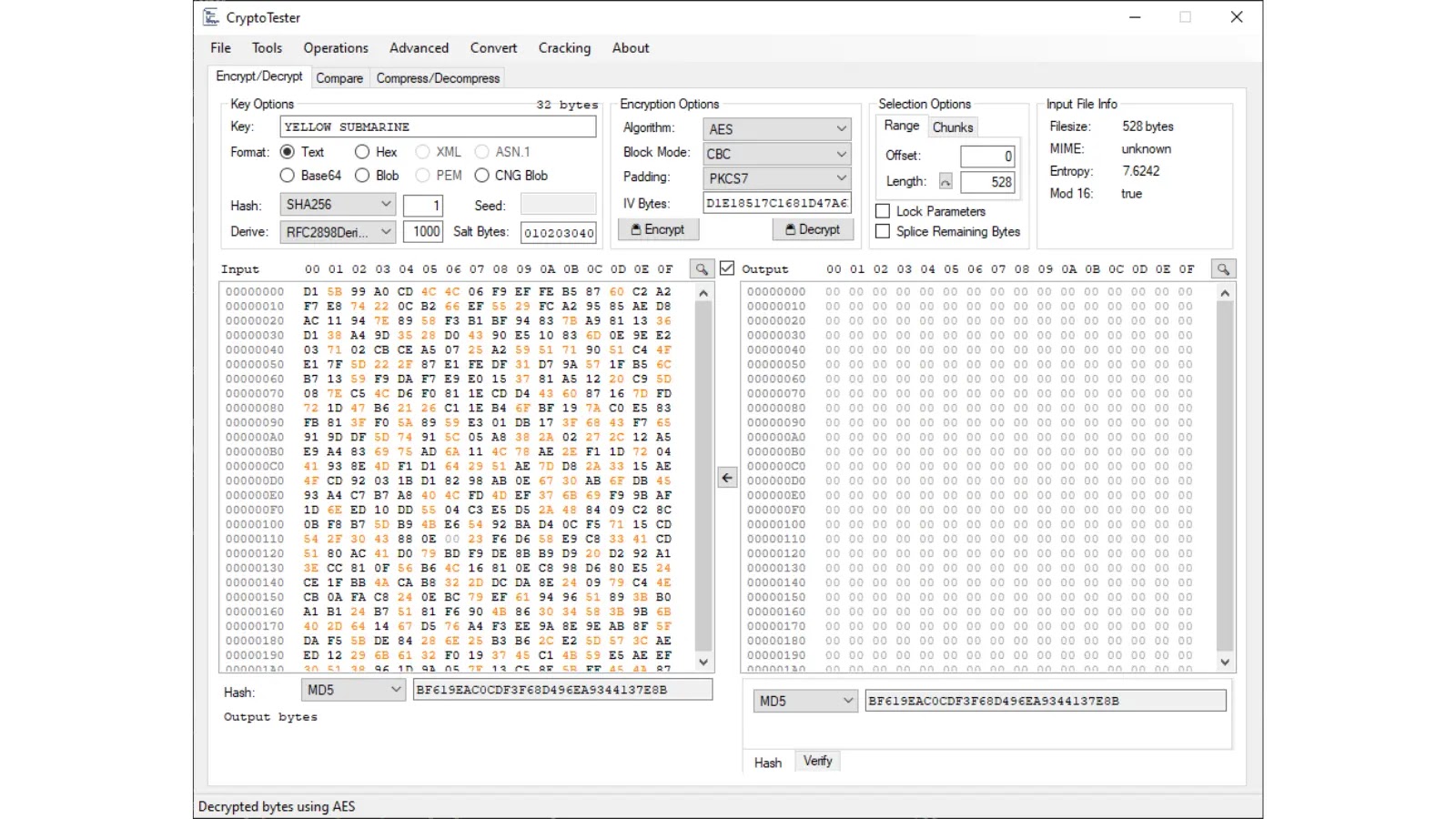
Encryption Options
Allows for selecting a cryptographic algorithm and its parameters, if supported.
Note: The IV Bytes (or Nonce, depending on algorithm) will automatically fill as 00 bytes of the appropriate length for the algorithm if it is left empty.
Selection Options
The input can be selected using two different modes: “Range” and “Chunks”.
Range
A simple range starting at Offset, and taking Length bytes.
The Length will automatically update whenever Input is changed, unless the Lock Parameters checkbox is ticked.
If you have made some calculations in the Length field, and wish to revert to the actual length of the Input, you can simply press the Reset Length button.
If Splice Remaining Bytes is ticked, then any bytes before Offset are prepended to the Output, and any bytes after Offset+Length are appended.
Chunks
Takes Take bytes, then skips Skip bytes, takes Take bytes, skips Skip bytes… until the end of Input. This can be used for ciphertext that is actually “interleaved” between chunks of plaintext.
The cryptographic algorithm is run on the resulting chunks as one sequential chunk, with no resetting of the key/IV/nonce etc.
If Splice Remaining Bytes is ticked, then any bytes in the Skip section are interleaved back into the Output.
Input File Info
This section displays simple information about the Input such as the filesize, detected MIME (if it is a file), total entropy, and whether it is divisible by 16 (a common block size).
Misc
The Input and Output views have synchronized scrolling; to disable this, uncheck the Syncronized scrolling checkbox between them.
The ???? button between the Input and Output can be used to move the Output to the Input view.
The Input or Output can be hashed using the respective dropdowns below their views. The Output can also have a verify algorithm ran on it (limited support for ECDSA currently).
Compare
This panel allows for comparing an encrypted file with its original. Both views support drag-and-drop, or File -> Open File can be used to open Original and Encrypted sequentially.
The Original view can also be filled using any of the File -> Input options; for example, comparing against a certain length of null bytes or the Windows sample picture Chrysanthemum.jpg.
The Original and Encrypted views have synchronized scrolling; to disable this, uncheck the Syncronized scrolling checkbox between them.
The ⇆ button between the Original and Encrypted views can be used to swap their contents.
Any bytes that differ between the two views will be displayed in dark red.
Original File / Encrypted File Info
Displays basic information on the Original and Encrypted views respectively.
Analysis
Once both views have been filled, a quick analysis is run against them.
- Hash Analysis: Checks if any hash of
Originalis present inEncrypted - Filename: Checks for common alterations to the filename (e.g. prepended/appended or encoded)
- BLOB Analysis: Checks for any CryptoAPI blobs present in
Encrypted - XOR Analysis: Checks for repeating blocks of XOR (or other simple ciphers)
- Filename Marker: Checks if the original filename is present in
Encrypted(UTF-8 or UTF-16) - Filesize Marker: Checks for the original filesize in
Encrypted(in various forms and encodings) - ASCII Marker / Analysis: Checks for an ASCII (or base64) marker at beginning or end of
Encrypted
Compress/Decompress
This panel allows for primitive use of a handful of compression algorithms, and has similiar functionality to the Encrypt/Decrypt panel.
Tools
Blob Analyzer
A tool for analyzing CryptoAPI blobs and CNG blobs.
BLOBs can be imported/exported to/from binary, base64, PEM, XML, and ASN.1 formats, where supported.
Tools
Additional blob-related tools which are activated only for supported blob types as applicable.
- Decrypt BLOB: Allows for decryption of a SIMPLEBLOB by inputting a PRIVATEKEYBLOB
- RSA Calculator: Loads the current RSA key into the RSA Calculator tool
- Repair BLOB: Repairs the BLOB if a recoverable corruption has been detected
- Blob Generator: Allows for generating any CryptoAPI blob
- Flip Endian: Flips the endianness of the key contents (may break the key!)
Blob Generator
Generates a CryptoAPI blob. The Bit Length is automatically updated with supported values for the selected aiKeyAlg. Note that some combinations of bType and aiKeyAlg are not valid, and will throw an error from the CryptoAPI provider.
Note: Keys are generated internally using CryptGenRandom, but I cannot guarantee the cryptographic security of using keys generated from this utility.
RSA Calculator
A tool for analyzing/calculating RSA keys. The seperate parameters of the key are displayed, and can be shown as decimal or hex. If enough parameters are present, the rest of the key can be calculated.
The key can be exported in various formats including a CryptoAPI blob, CNG blob, PEM, XML, and ASN.1, either to file, clipboard, or the Main Window (Encrypt/Decrypt). Additionally, if exporting to the Main Window, the raw integers can be exported for the Raw RSA algorithm.
Key Finder
A tool that searches a file for a cryptographic key in several formats.
Examples of supported formats:
- CryptoAPI blob
- CNG blob
- ASN.1 blob
- NTRU blob
- All of the above as ASCII hex strings
- All of the above as base64 (or damaged base64)
- PEM keys
- XML keys
- Raw RSA modulus and exponent as hex strings
RNG Tester
A tool for testing various known PRNG algorithms.
Seed Options
Set the starting Seed for the PRNG.
RNG Options
Set the PRNG Algorithm, along with the Length of outputs to produce, and an optional Modulus to apply to each output. For example, a Modulus of xFF can be used to cast each output to a byte.
Output
- Format: Format to output each random number as
If Alpha is selected:
- Charset: A character set to map against each random number
- Presets: Common preset charsets to autofill
- Skip Chars: If a character in this list would be output, it is skipped, and the next random number polled
The entropy of the produced output is also displayed for Alpha output. This is a rough estimate of entropy (or number of possibilities) for blindly bruteforcing the output (without directly attacking the PRNG).
Base Encoder
A tool for using different base encodings. Supports standard preset charsets, or supply your own custom charset.
With the exception of encoders that use a checksum (e.g. Bitcoin’s Base58Check), decoding is done without verifying the padding, so even partial or damaged encodings will be decoded raw.
String Encoder
A tool for viewing text or bytes as ASCII, UTF-8, and UTF-16 simultaneously.
ECC Validator
A tool for validating elliptical curve points. Can import/export from/to an ECPoint (uncompressed or compressed forms), PEM, or CNG blob.
Operations
Various operations to be performed based on the current panel.
XOR Files / AND Files
Takes the Original and Encrypted from the Compare panel, and applies the XOR or AND operation, and displays a stream.
Generate Keystream
Uses the algorithm information from the Encrypt/Decrypt panel and generates a keystream of given length to save to file.
Visual Difference
Displays a graphical chart of difference between pixels in the Compare panel.
Bruteforce Algorithm
Uses the provided key material and Input from the Encrypt/Decrypt panel, and a given expected output, and enumerates all possible options in the Encryption Options section to try and find a match.
Bruteforce Keys
This tool can be used to test a list or folder of known keys against the Input using the specified cipher parameters.
- Key File Format: Specify the expected format for the input, such as a base64-encoded key per line, or take
Byte Countbytes of the file at a time. - Expected Output: The expected output as bytes, or simply any non-null output (should only be used with valid padding schemes)
If a key is successfully matched, the Select button will be activated to allow passing the key and its parameters to the main window.
Attempt Blind Decryption
Using the blocksize of the selected cipher, enumerates over every possible block and attempts decryption using the specified key.
Example: You have an RSA-2048 private key, and a 0x1000 byte blob of possible ciphertext as Input. Using this operation will try decrypting Input[0x00:0x100], then Input[0x01:0x101], then Input[0x02:0x102] etc…
Note: This operation currently only supports the RSA algorithm. It is also limited to a max of 10000 input bytes.
Advanced
Little Endian
Use little endian internally (if algorithm supports it).
Custom
Allows for setting custom parameters if selected algorithm supports any. For example, the Salsa20 family of algorithms support custom rounds, constant, position, or inputting a raw matrix.
IV
Options for the IV, such as inputting from text or base64, and recovering an IV from known plaintext.
Presets
Presets for certain encryption schemes, e.g. OpenSSL.
Convert
Small tools for conversions.
DWORD ⇆ Integer
Convert an integer to DWORD, or DWORD bytes to integer.
Hex ⇆ Integers
Convert hex bytes to a list of integers, or a list of integers to bytes. Spaces and commas for the output can be optionally set.

























.webp)

