S3TK is a security toolkit for Amazon S3.

Installation
Run:
pip install s3tk
You can use the AWS CLI to set up your AWS credentials:
pip install awscli
aws configure
Commands
Scan
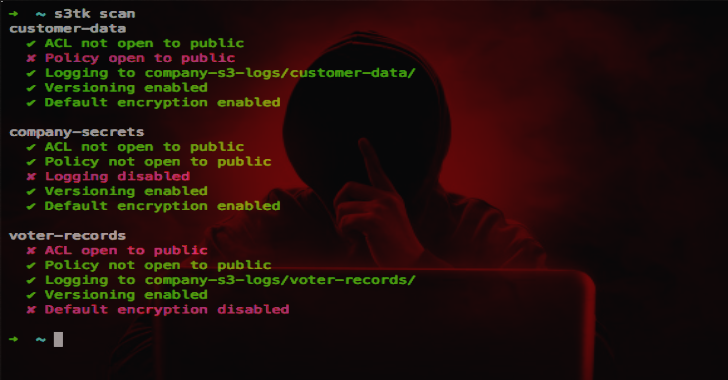
Scan your buckets for:
- ACL open to public
- policy open to public
- logging enabled
- versioning enabled
- default encryption enabled
s3tk scan
Only run on specific buckets
s3tk scan my-bucket my-bucket-2
Also works with wildcards
s3tk scan “my-bucket*”
Confirm correct log bucket(s) and prefix
s3tk scan –log-bucket my-s3-logs –log-bucket other-region-logs –log-prefix “{bucket}/”
Skip logging, versioning, or default encryption
s3tk scan –skip-logging –skip-versioning –skip-default-encryption
Get email notifications of failures (via SNS)
s3tk scan –sns-topic arn:aws:sns:…
Also Read – Quark Engine : An Obfuscation-Neglect Android Malware Scoring System
List Policy
List bucket policies
s3tk list-policy
Only run on specific buckets
s3tk list-policy my-bucket my-bucket-2
Show named statements
s3tk list-policy –named
Set Policy
Note: This replaces the previous policy
Only private uploads
s3tk set-policy my-bucket –no-object-acl
Delete Policy
Delete policy
s3tk delete-policy my-bucket
Enable Logging
Enable logging on all buckets
s3tk enable-logging –log-bucket my-s3-logs
Only on specific buckets
s3tk enable-logging my-bucket my-bucket-2 –log-bucket my-s3-logs
Set log prefix ({bucket}/ by default)
s3tk enable-logging –log-bucket my-s3-logs –log-prefix “logs/{bucket}/”
Use the --dry-run flag to test
A few notes about logging:
- buckets with logging already enabled are not updated at all
- the log bucket must in the same region as the source bucket – run this command multiple times for different regions
- it can take over an hour for logs to show up
Enable Versioning
Enable versioning on all buckets
s3tk enable-versioning
Only on specific buckets
s3tk enable-versioning my-bucket my-bucket-2
Use the --dry-run flag to test
Enable Default Encryption
Enable default encryption on all buckets
s3tk enable-default-encryption
Only on specific buckets
s3tk enable-default-encryption my-bucket my-bucket-2
This does not encrypt existing objects – use the encrypt command for this
Use the --dry-run flag to test
Scan Object ACL
Scan ACL on all objects in a bucket
s3tk scan-object-acl my-bucket
Only certain objects
s3tk scan-object-acl my-bucket –only “*.pdf”
Except certain objects
s3tk scan-object-acl my-bucket –except “*.jpg”
Reset Object ACL
Reset ACL on all objects in a bucket
s3tk reset-object-acl my-bucket
This makes all objects private. See bucket policies for how to enforce going forward.
Use the --dry-run flag to test
Specify certain objects the same way as scan-object-acl
Encrypt
Encrypt all objects in a bucket with server-side encryption
s3tk encrypt my-bucket
Use S3-managed keys by default. For KMS-managed keys, use:
s3tk encrypt my-bucket –kms-key-id arn:aws:kms:…
For customer-provided keys, use:
s3tk encrypt my-bucket –customer-key secret-key
Use the --dry-run flag to test
Specify certain objects the same way as scan-object-acl
Note: Objects will lose any custom ACL
Delete Unencrypted Versions
Delete all unencrypted versions of objects in a bucket
s3tk delete-unencrypted-versions my-bucket
For safety, this will not delete any current versions of objects
Use the --dry-run flag to test
Specify certain objects the same way as scan-object-acl
Scan DNS
Scan Route 53 for buckets to make sure you own them
s3tk scan-dns
Otherwise, you may be susceptible to subdomain takeover
Credentials
Credentials can be specified in ~/.aws/credentials or with environment variables. See this guide for an explanation of environment variables.
You can specify a profile to use with:
AWS_PROFILE=your-profile s3tk
Upgrading
Run:
pip install s3tk –upgrade
To use master, run:
pip install git+https://github.com/ankane/s3tk.git –upgrade
Docker
Run:
docker run -it ankane/s3tk aws configure
Commit your credentials:
docker commit $(docker ps -l -q) my-s3tk
And run:
docker run -it my-s3tk s3tk scan